Increased plasma and tissue MMP levels are associated with BCSFB and BBB disruption evident on post-contrast FLAIR after experimental stroke
- PMID: 20197780
- PMCID: PMC2879459
- DOI: 10.1038/jcbfm.2010.1
Increased plasma and tissue MMP levels are associated with BCSFB and BBB disruption evident on post-contrast FLAIR after experimental stroke
Abstract
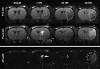
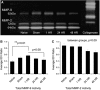
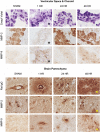
In this study, we examined the relationship between tissue and blood levels of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 through gelatin zymography at multiple time points after experimental stroke. We additionally investigated the association between these levels and the evidence of blood-cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) barrier (BCSFB) and blood-brain barrier (BBB) disruption on post-contrast fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery (FLAIR) imaging. Increased plasma MMP-9 was associated with BCSFB disruption at 1h post-reperfusion. Ventricular enhancement ipsilateral to the stroke was 500+/-100%, significantly higher than sham, 24, and 48 h groups. Increased tissue MMP-2 and MMP-9 were associated with BBB disruption at 48 h post-reperfusion. Parenchymal enhancement was 60+/-20% for a volume equivalent to 260+/-80 mm(3). Although the percent enhancement was comparable across groups, the volume of enhancing lesion was significantly higher at 48 h (260+/-80 mm(3), 100%) in comparison to 1 h (8+/-3 mm(3), 3%) and 24 h (51 mm(3), 18%). These findings support the use of imaging markers of BCSFB and BBB status as indirect measures of MMP regulation in the blood and brain tissue. The methods presented herein should be useful in understanding the link between MMPs, barrier integrity, and subsequent hemorrhagic transformation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Blood-brain barrier disruption in humans is independently associated with increased matrix metalloproteinase-9.Stroke. 2010 Mar;41(3):e123-8. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.570515. Epub 2009 Dec 24. Stroke. 2010. PMID: 20035078 Free PMC article.
-
MMPs/TIMPs imbalances in the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid are associated with the pathogenesis of HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorders.Brain Behav Immun. 2017 Oct;65:161-172. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.04.024. Epub 2017 May 6. Brain Behav Immun. 2017. PMID: 28487203 Free PMC article.
-
Rutin improves functional outcome via reducing the elevated matrix metalloproteinase-9 level in a photothrombotic focal ischemic model of rats.J Neurol Sci. 2014 Apr 15;339(1-2):75-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2014.01.024. Epub 2014 Jan 24. J Neurol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24507948
-
Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases to reduce blood brain barrier disruption and haemorrhagic transformation in ischaemic stroke: Go broad or go narrow?Neuropharmacology. 2025 Jan 1;262:110192. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.110192. Epub 2024 Oct 16. Neuropharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39419277 Review.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9): A macromolecular mediator in CNS infections: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Jun;311(Pt 2):143902. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.143902. Epub 2025 May 4. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40328391 Review.
Cited by
-
Amyloid β Oligomers Disrupt Blood-CSF Barrier Integrity by Activating Matrix Metalloproteinases.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 16;35(37):12766-78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0006-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26377465 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms and gene expression of metalloproteinases and their inhibitors associated with cerebral ischemic stroke in young patients with sickle cell anemia.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Apr;50(4):3341-3353. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08262-2. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36720795
-
Choroid plexus and the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier in disease.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020 May 6;17(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12987-020-00196-2. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2020. PMID: 32375819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation between neutrophil-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (NHR) and adverse prognosis in patients who achieve complete recanalization after thrombectomy for acute large vessel occlusion stroke.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1536535. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1536535. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40534744 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture ameliorates post-stroke learning and memory through minimizing ultrastructural brain damage and inhibiting the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jul;14(1):225-33. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5227. Epub 2016 May 9. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27177163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barone FC, Price WJ, White RF, Willette RN, Feuerstein GZ. Genetic hypertension and increased susceptibility to cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 1992;16:219–233. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron M, Ferriero DM, Vreman HJ, Stevenson DK, Sharp FR. Hypoxia-ischemia, but not hypoxia alone, induces the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HSP32) in newborn rat brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:647–658. - PubMed
-
- del Zoppo GJ, Milner R, Mabuchi T, Hung S, Wang X, Berg GI, Koziol JA. Microglial activation and matrix protease generation during focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2007;38:646–651. - PubMed
-
- Ennis SR, Keep RF. The effects of cerebral ischemia on the rat choroid plexus. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2006;26:675–683. - PubMed
-
- Garcia JH, Wagner S, Liu KF, Hu XJ. Neurological deficit and extent of neuronal necrosis attributable to middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Statistical validation. Stroke. 1995;26:627–635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

