Intracortical cartography in an agranular area
- PMID: 20198150
- PMCID: PMC2796917
- DOI: 10.3389/neuro.01.030.2009
Intracortical cartography in an agranular area
Abstract
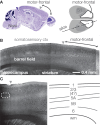
A well-defined granular layer 4 is a defining cytoarchitectonic feature associated with sensory areas of mammalian cerebral cortex, and one with hodological significance: the local axons ascending from cells in thalamorecipient layer 4 and connecting to layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons form a major feedforward excitatory interlaminar projection. Conversely, agranular cortical areas, lacking a distinct layer 4, pose a hodological conundrum: without a laminar basis for the canonical layer 4-->2/3 pathway, what is the basic circuit organization? This review highlights current challenges and prospects for local-circuit electroanatomy and electrophysiology in agranular cortex, focusing on the mouse. Different lines of evidence, drawn primarily from studies of motor areas in frontal cortex in rodents, support the view that synaptic circuits in agranular cortex are organized around prominent descending excitatory layer 2/3-->5 pathways targeting multiple classes of projection neurons.
Keywords: frontal; motor; pyramidal neuron; synaptic circuits.
Figures

References
-
- Brecht M., Krauss A., Muhammad S., Sinai-Esfahani L., Bellanca S., Margrie T. W. (2004). Organization of rat vibrissa motor cortex and adjacent areas according to cytoarchitectonics, microstimulation, and intracellular stimulation of identified cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 479, 360–37310.1002/cne.20306 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

