Effects of nebivolol versus bisoprolol on endothelial function in hypertensive patients
- PMID: 20198199
- PMCID: PMC2827212
Effects of nebivolol versus bisoprolol on endothelial function in hypertensive patients
Abstract
Objective: To determine the effects of two beta-blockers, nebivolol and bisoprolol, on endothelial function in newly diagnosed hypertensive patients.
Methods: Twenty-five hypertensive patients with a mean (+/- SD) age of 45.3+/-11.5 years were randomly assigned to receive either nebivolol or bisoprolol for eight weeks in an open-label, crossover design. Flow-mediated endothelial-dependent vasodilation (FMD) was measured at baseline and after each eight-week treatment period. At the end of each treatment period, 24 h ambulatory blood pressure (BP) monitoring was performed.
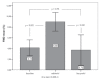
Results: The effect of the two beta-blockers on BP was similar. The mean FMD before initiation of treatment was 4.14+/-3.55%. After treatment with nebivolol, FMD increased to 8.99+/-4.21%, with a statistically significant difference from baseline (P<0.001). The effect of bisoprolol treatment on FMD was not as dramatic (3.72+/-6.84%), with no statistically significant difference from baseline. Comparing FMD after each therapeutic regimen, nebivolol treatment resulted in a marked increase in the reactivity of the brachial artery (ie, improvement of endothelial function) compared with bisoprolol treatment (P<0.001).
Conclusion: Nebivolol treatment of untreated hypertensive patients led to a significant improvement in endothelial function compared with bisoprolol treatment, despite the similar effect on BP with either therapeutic agent.
Keywords: Arterial hypertension; Bisoprolol; Endothelial function; Flow-mediated dilation; Nebivolol.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Effect of Nebivolol and Bisoprolol on Sexual Function of Hypertensive Female Patients.Cureus. 2021 May 16;13(5):e15062. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15062. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34141506 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of the beta1-selectivity of three beta1-selective beta-blockers.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2003 Jun;28(3):179-86. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2710.2003.00477.x. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2003. PMID: 12795776 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of nebivolol and atenolol on brachial artery flow-mediated vasodilation in patients with coronary artery disease.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2005 Aug;19(4):277-81. doi: 10.1007/s10557-005-3117-9. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2005. PMID: 16187009 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical pharmacodynamics of nebivolol: new evidence of nitric oxide-mediated vasodilating activity and peculiar haemodynamic properties in hypertensive patients.Blood Press Suppl. 2004 Oct;1:17-32. doi: 10.1080/08038020410016548. Blood Press Suppl. 2004. PMID: 15587108 Review.
-
Effects of nebivolol versus other antihypertensive drugs on the endothelial dysfunction in patients with essential hypertension.Biosci Rep. 2020 May 29;40(5):BSR20200436. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200436. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32342981 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hypertension treatment in the Asia-Pacific: the role of and treatment strategies with nebivolol.Heart Asia. 2016 Feb 24;8(1):22-6. doi: 10.1136/heartasia-2015-010656. eCollection 2016. Heart Asia. 2016. PMID: 27326226 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Properties of Highly Selective β-blockers With or Without Additional Vasodilator Properties: Focus on Bisoprolol and Nebivolol in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022 Oct;36(5):959-971. doi: 10.1007/s10557-021-07205-y. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022. PMID: 34106365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Effect of Nebivolol and Bisoprolol on Sexual Function of Hypertensive Female Patients.Cureus. 2021 May 16;13(5):e15062. doi: 10.7759/cureus.15062. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34141506 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of nebivolol monotherapy or combination therapy on blood pressure levels in patients with hypertension: an updated systematic review and multilevel meta-analysis of 91 randomized controlled trials.High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2025 Jan;32(1):7-31. doi: 10.1007/s40292-024-00687-5. Epub 2024 Oct 29. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev. 2025. PMID: 39467996
-
Comparative Efficacy of Antihypertensive Agents in Flow-Mediated Vasodilation of Patients with Hypertension: Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial.Int J Hypertens. 2022 Apr 30;2022:2432567. doi: 10.1155/2022/2432567. eCollection 2022. Int J Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 35535214 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. European Society of Hypertension; European Society of Cardiology 2007 ESH-ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Blood Press. 2007;16:135–232. - PubMed
-
- Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Gooch VM, et al. Non-invasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet. 1992;340:1111–5. - PubMed
-
- Ercan E, Tengiz I, Ercan HE, Nalbantgil I. Left ventricular hypertrophy and endothelial functions in patients with essential hypertension. Coron Artery Dis. 2003;14:541–4. - PubMed
-
- Millgard J, Lind L. Acute hypertension impairs endothelium-dependent vasodilation. Clin Sci (Lond) 1999;96:217–8. - PubMed
-
- Palmieri V, Storto G, Arezzi E, et al. Relations of left ventricular mass and systolic function to endothelial function and coronary flow reserve in healthy, new discovered hypertensive subjects. J Hum Hypertens. 2005;19:941–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
