Radiation-inducible silencing of uPA and uPAR in vitro and in vivo in meningioma
- PMID: 20198323
- PMCID: PMC2837517
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo_00000557
Radiation-inducible silencing of uPA and uPAR in vitro and in vivo in meningioma
Abstract
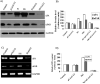
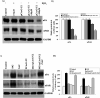
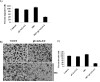
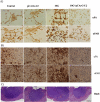
Stereospecific radiation treatment offers a distinct opportunity for temporal and spatial regulation of gene expression at tumor sites by means of inducible promoters. To this end, a plasmid, pCArG-U2, was constructed by incorporating nine CArG elements (in tandem) of EGR1 gene upstream to uPA and uPAR siRNA oligonucleotides in a pCi-neo vector. Radiation-induced siRNA expression was detected in a meningioma cell line (IOMM-Lee). Immunoblotting and RT-PCR analyses confirmed downregulation of uPA and uPAR. A similar effect was observed in transfected cells followed by H2O2 treatment. Moreover, pre-treatment of transfected cells with N-acetyl L-cysteine blocked the silencing of uPA and uPAR, which further confirmed the oxidative damage-mediated downregulation. Cell proliferation assays and Western blot analysis for apoptotic molecules confirmed cell death in a radiation-inducible fashion. Migration and matrigel invasion assays also revealed a marked decrease in migration and invasion. Immunocytochemistry showed a marked decrease in uPA and uPAR levels in transfected and irradiated cells. H&E staining revealed a decrease in the pre-established tumor volume among the animals treated with pCArG-U2 and radiation. Immunohistochemistry of the brain sections established with intracranial tumors also revealed a marked decrease in uPA and uPAR in a radiation-inducible fashion. Taken together, our data suggest pCArG-U2 as a suitable candidate for radiation-inducible gene therapy.
Figures
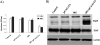
References
-
- Park CM, Park MJ, Kwak HJ, Lee HC, Kim MS, Lee SH, Park IC, Rhee CH, Hong SI. Ionizing Radiation Enhances Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Secretion and Invasion of Glioma Cells through Src/Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mediated p38/Akt and Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Signaling Pathways. Cancer Res. 2006;66:8511–8519. - PubMed
-
- Zhai GG, Malhotra R, Delaney M, Latham D, Nestler U, Zhang M, Mukherjee N, Song Q, Robe P, Chakravarti A. Radiation enhances the invasive potential of primary glioblastoma cells via activation of the Rho signaling pathway. J Neurooncol. 2006;76:227–237. - PubMed
-
- Scott SD, Marples B, Hendry JH, Lashford LS, Embleton MJ, Hunter RD, Howell A, Margison GP. A radiation-controlled molecular switch for use in gene therapy of cancer. Gene Ther. 2000;7:1121–1125. - PubMed
-
- Worthington J, McCarthy HO, Barrett E, Adams C, Robson T, Hirst DG. Use of the radiation-inducible WAF1 promoter to drive iNOS gene therapy as a novel anti-cancer treatment. J Gene Med. 2004;6:673–680. - PubMed
-
- Marignol L, Coffey M, Hollywood D, Lawler M. Radiation to control transgene expression in tumors. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007;6:1005–1012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

