A novel seven-octapeptide repeat insertion in the prion protein gene (PRNP) in a Dutch pedigree with Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease phenotype: comparison with similar cases from the literature
- PMID: 20198483
- PMCID: PMC3015204
- DOI: 10.1007/s00401-010-0656-3
A novel seven-octapeptide repeat insertion in the prion protein gene (PRNP) in a Dutch pedigree with Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease phenotype: comparison with similar cases from the literature
Abstract
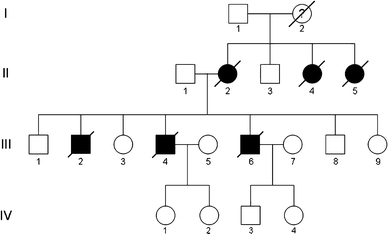
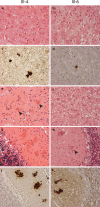
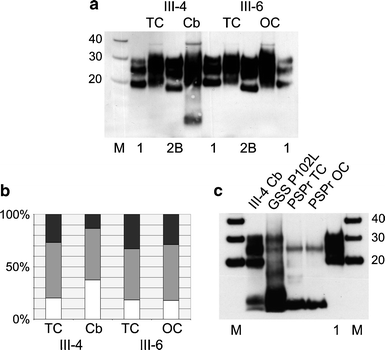
Human prion diseases can be sporadic, inherited or acquired by infection and show considerable phenotypic heterogeneity. We describe the clinical, histopathological and pathological prion protein (PrP(Sc)) characteristics of a Dutch family with a novel 7-octapeptide repeat insertion (7-OPRI) in PRNP, the gene encoding the prion protein (PrP). Clinical features were available in four, neuropathological features in three and biochemical characteristics in two members of this family. The clinical phenotype was characterized by slowly progressive cognitive decline, personality change, lethargy, depression with anxiety and panic attacks, apraxia and a hypokinetic-rigid syndrome. Neuropathological findings consisted of numerous multi- and unicentric amyloid plaques throughout the cerebrum and cerebellum with varying degrees of spongiform degeneration. Genetic and molecular studies were performed in two male family members. One of them was homozygous for valine and the other heterozygous for methionine and valine at codon 129 of PRNP. Sequence analysis identified a novel 168 bp insertion [R2-R2-R2-R2-R3g-R2-R2] in the octapeptide repeat region of PRNP. Both patients carried the mutation on the allele with valine at codon 129. Western blot analysis showed type 1 PrP(Sc) in both patients and detected a smaller ~8 kDa PrP(Sc) fragment in the cerebellum in one patient. The features of this Dutch kindred define an unusual neuropathological phenotype and a novel PRNP haplotype among the previously documented 7-OPRI mutations, further expanding the spectrum of genotype-phenotype correlations in inherited prion diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A second case of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease linked to the G131V mutation in the prion protein gene in a Dutch patient.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2011 Aug;70(8):698-702. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182270c54. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21760536
-
Unusual clinical and molecular-pathological profile of gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease associated with a novel PRNP mutation (V176G).JAMA Neurol. 2013 Sep 1;70(9):1180-5. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.165. JAMA Neurol. 2013. PMID: 23857164
-
Prion protein amyloidosis with divergent phenotype associated with two novel nonsense mutations in PRNP.Acta Neuropathol. 2010 Feb;119(2):189-97. doi: 10.1007/s00401-009-0609-x. Epub 2009 Nov 13. Acta Neuropathol. 2010. PMID: 19911184 Free PMC article.
-
Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;724:128-37. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0653-2_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22411239 Review.
-
Prion encephalopathy with insertion of octapeptide repeats: the number of repeats determines the type of cerebellar deposits.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1998 Apr;24(2):125-30. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2990.1998.00098.x. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1998. PMID: 9634208 Review.
Cited by
-
Small-molecule theranostic probes: a promising future in neurodegenerative diseases.Int J Cell Biol. 2013;2013:150952. doi: 10.1155/2013/150952. Epub 2013 Nov 12. Int J Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 24324497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prion disease: experimental models and reality.Acta Neuropathol. 2017 Feb;133(2):197-222. doi: 10.1007/s00401-017-1670-5. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Acta Neuropathol. 2017. PMID: 28084518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus) infected with the agent of bovine spongiform encephalopathy develop tau pathology.J Comp Pathol. 2012 Jul;147(1):84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2011.09.004. Epub 2011 Oct 20. J Comp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22018806 Free PMC article.
-
Amino Acid Substitution within Seven-Octapeptide Repeat Insertions in the Prion Protein Gene Associated with Short-Term Course.Viruses. 2022 Oct 13;14(10):2245. doi: 10.3390/v14102245. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36298800 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the unfolded protein response and granulovacuolar degeneration are not common features of human prion pathology.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016 Oct 28;4(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s40478-016-0383-7. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2016. PMID: 27793194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown P, Goldfarb LG, McCombie WR, et al. Atypical Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in an American family with an insert mutation in the PRNP amyloid precursor gene. Neurology. 1992;42:422–427. - PubMed
-
- Capellari S, Vital C, Parchi P, et al. Familial prion disease with a novel 144-bp insertion in the prion protein gene in a Basque family. Neurology. 1997;49:133–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

