Tumor necrosis factor-mediated cell death: to break or to burst, that's the question
- PMID: 20198502
- PMCID: PMC11115929
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-010-0283-0
Tumor necrosis factor-mediated cell death: to break or to burst, that's the question
Abstract
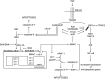
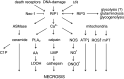
In this review, we discuss the signal-transduction pathways of three major cellular responses induced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF): cell survival through NF-kappaB activation, apoptosis, and necrosis. Recruitment and activation of caspases plays a crucial role in the initiation and execution of TNF-induced apoptosis. However, experimental inhibition of caspases reveals an alternative cell death pathway, namely necrosis, also called necroptosis, suggesting that caspases actively suppress the latter outcome. TNF-induced necrotic cell death crucially depends on the kinase activity of receptor interacting protein serine-threonine kinase 1 (RIP1) and RIP3. It was recently demonstrated that ubiquitination of RIP1 determines whether it will function as a pro-survival or pro-cell death molecule. Deeper insight into the mechanisms that control the molecular switches between cell survival and cell death will help us to understand why TNF can exert so many different biological functions in the etiology and pathogenesis of human diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Clarke PG. Developmental cell death: morphological diversity and multiple mechanisms. Anat Embryol (Berl) 1990;181:195–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

