Prolyl 4-hydroxylase
- PMID: 20199358
- PMCID: PMC2841224
- DOI: 10.3109/10409231003627991
Prolyl 4-hydroxylase
Abstract
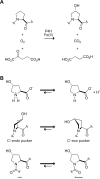
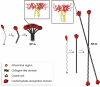
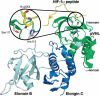
Posttranslational modifications can cause profound changes in protein function. Typically, these modifications are reversible, and thus provide a biochemical on-off switch. In contrast, proline residues are the substrates for an irreversible reaction that is the most common posttranslational modification in humans. This reaction, which is catalyzed by prolyl 4-hydroxylase (P4H), yields (2S,4R)-4-hydroxyproline (Hyp). The protein substrates for P4Hs are diverse. Likewise, the biological consequences of prolyl hydroxylation vary widely, and include altering protein conformation and protein-protein interactions, and enabling further modification. The best known role for Hyp is in stabilizing the collagen triple helix. Hyp is also found in proteins with collagen-like domains, as well as elastin, conotoxins, and argonaute 2. A prolyl hydroxylase domain protein acts on the hypoxia inducible factor alpha, which plays a key role in sensing molecular oxygen, and could act on inhibitory kappaB kinase and RNA polymerase II. P4Hs are not unique to animals, being found in plants and microbes as well. Here, we review the enzymic catalysts of prolyl hydroxylation, along with the chemical and biochemical consequences of this subtle but abundant posttranslational modification.
Figures



References
-
- Adefarati AA, Giacobbe RA, Hensens OD, Tkacz JS. Biosynthesis of l-671,329, and echinocandin-type antibiotic produced by Zalerion arboricola: Origins of some of the unusual amino acids and the dimethylmyristic acid side chain. J Am Chem Soc. 1991;113:3542–3545.
-
- Aldunate R, Casar JC, Brandan E, Inestrosa NC. Structural and functional organization of synaptic acetylcholinesterase. Brain Res Rev. 2004;47:96–104. - PubMed
-
- Annunen P, Helaakoski T, Myllyharju J, Veijola J, Pihlajaniemi T, Kivirikko KI. Cloning of the human prolyl 4-hydroxylase α subunit isoform α(II) and characterization of the type II enzyme tetramer. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:17342–17348. - PubMed
-
- Atreya PL, Ananthanarayanan VS. Interaction of prolyl 4-hydroxylase with synthetic peptide substrates: A conformational model for collagen proline hydroxylation. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:2852–2858. - PubMed
-
- Bächinger HP. The influence of peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerase on the in vitro folding of type III collagen. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:17144–17148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
