mot-2-Mediated cross talk between nuclear factor-B and p53 is involved in arsenite-induced tumorigenesis of human embryo lung fibroblast cells
- PMID: 20199942
- PMCID: PMC2920912
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.0901677
mot-2-Mediated cross talk between nuclear factor-B and p53 is involved in arsenite-induced tumorigenesis of human embryo lung fibroblast cells
Abstract
Background: Inactivation of p53 is involved in arsenite-induced tumorigenesis; however, the molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood.
Objective: We investigated the molecular mechanisms underlying the inactivation of p53 and neoplastic transformation induced by arsenite in human embryo lung fibroblast (HELF) cells.
Methods: Anchorage-independent growth assays were performed, and tumorigenicity in intact animals was assessed to confirm arsenite-induced neoplastic transformation. We determined the levels and functions of p53, nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-B; a key transcriptional regulator), and mot-2 (a p53 inhibitor) and their relationships in arsenite-induced transformed HELF cells by two-dimensional electrophoresis, reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, Western blot, immunofluorescence, and co-immunoprecipitation assays.
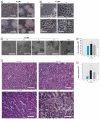
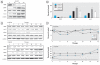
Results: Exposure of HELF cells to low levels of arsenite increased their proliferation rate and anchorage-independent growth and disrupted normal contact inhibition. When introduced into nude mice, transformed cells were tumorigenic. We used proteomic analysis to identify proteins with altered expression between untreated and arsenite-exposed cells. We found decreased expression of NF-B repressing factor (NKRF; an inhibitor of NF-B-mediated gene transcription), increased expression of mot-2, and increased activation of NF-B. Changes in cells exposed to 1.0 microM arsenite were more marked than changes in cells exposed to 0.5 or 2.0 microM arsenite. Inactivation of NF-B prevented malignant transformation induced by 1.0 microM arsenite. Moreover, we also identified a mechanism whereby NF-B regulated p53. Specifically, activation of NF-B up-regulated mot-2 expression, which prevented nuclear translocation of p53 and switched the binding preference of the p53 and NF-B coactivator CBP [cyclic AMP-responsive element binding protein (CREB) binding protein] from p53 to NF-B.
Conclusions: mot-2-mediated cross talk between NF-B and p53 appears to be involved in arsenite-induced tumorigenesis of HELF cells.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Feedback regulations of miR-21 and MAPKs via Pdcd4 and Spry1 are involved in arsenite-induced cell malignant transformation.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057652. Epub 2013 Mar 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469214 Free PMC article.
-
The repressive effect of NF-kappaB on p53 by mot-2 is involved in human keratinocyte transformation induced by low levels of arsenite.Toxicol Sci. 2010 Jul;116(1):174-82. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq109. Epub 2010 Apr 7. Toxicol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20375080
-
Opposed arsenite-mediated regulation of p53-survivin is involved in neoplastic transformation, DNA damage, or apoptosis in human keratinocytes.Toxicology. 2012 Oct 28;300(3):121-31. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.06.004. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Toxicology. 2012. PMID: 22706169
-
Regulation of miRNA-21 by reactive oxygen species-activated ERK/NF-κB in arsenite-induced cell transformation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 May 1;52(9):1508-18. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.02.020. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012. PMID: 22387281
-
Nuclear factor-κB, p53, and mitochondria: regulation of cellular metabolism and the Warburg effect.Trends Biochem Sci. 2012 Aug;37(8):317-24. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2012.04.002. Epub 2012 May 23. Trends Biochem Sci. 2012. PMID: 22626470 Review.
Cited by
-
Involvement and Targeted Intervention of Mortalin-Regulated Proteome Phosphorylated-Modification in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 29;11:687871. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.687871. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34395254 Free PMC article.
-
A MALAT1/HIF-2α feedback loop contributes to arsenite carcinogenesis.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 2;7(5):5769-87. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6806. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26735578 Free PMC article.
-
Why is Mortalin a Potential Therapeutic Target for Cancer?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 29;10:914540. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.914540. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35859897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Feedback regulations of miR-21 and MAPKs via Pdcd4 and Spry1 are involved in arsenite-induced cell malignant transformation.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057652. Epub 2013 Mar 1. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469214 Free PMC article.
-
Arsenic trioxide reverses the chemoresistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: a targeted intervention of 14-3-3η/NF-κB feedback loop.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Dec 20;37(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-1005-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30572915 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aylon Y, Oren M. Living with p53, dying of p53. Cell. 2007;130(4):597–600. - PubMed
-
- Bodwell JE, Kingsley LA, Hamilton JW. Arsenic at very low concentrations alters glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-mediated gene activation but not GR-mediated gene repression: complex dose-response effects are closely correlated with levels of activated GR and require a functional GR DNA binding domain. Chem Res Toxicol. 2004;17(8):1064–1076. - PubMed
-
- Chen CL, Hsu LI, Chiou HY, Hsueh YM, Chen SY, Wu MM, et al. Ingested arsenic, cigarette smoking, and lung cancer risk: a follow-up study in arseniasis-endemic areas in Taiwan. JAMA. 2004;292(24):2984–2990. - PubMed
-
- Gao A, Liu B, Shi X, Jia X, Ye M, Jiao S, et al. Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt/p70S6K/AP-1 signaling pathway mediated benzo(a)pyrene-induced cell cycle alternation via cell cycle regulatory proteins in human embryo lung fibroblasts. Toxicol Lett. 2007;170(1):30–41. - PubMed
-
- Hayflick L, Moorhead PS. The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp Cell Res. 1961;25:585–621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

