The effect of progressive glomerular disease on megalin-mediated endocytosis in the kidney
- PMID: 20200006
- PMCID: PMC2910335
- DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfq044
The effect of progressive glomerular disease on megalin-mediated endocytosis in the kidney
Abstract
Background: A well-characterized dog model of the X-linked collagen disease Alport syndrome (XLAS) was used to study the effect of progressive glomerular disease on megalin-mediated endocytosis. In XLAS, altered structure and function of the glomerular basement membrane induces a progressive proteinuric nephropathy.
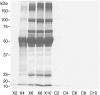
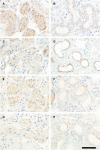
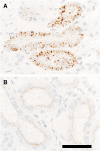
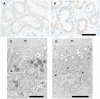
Methods: The investigation was performed in male XLAS dogs and age-matched normal male littermates. The urine profile and megalin-mediated endocytosis in the proximal tubule of six healthy and six XLAS dogs were examined at 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 months of age using SDS-PAGE, immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry.
Results: Gradually increasing urinary excretion of proteins over time and a reduced content of the same proteins in proximal tubule cells were found. Besides the glomerular component of the proteinuria, a significant tubular component was seen, which is due to a progressive change in the uptake of low-molecular-weight (LMW) ligands by megalin. Furthermore, the protein overload present in the lumen of the proximal tubule exceeds the reabsorption capacity of megalin and the co-receptor cubilin and results in a combined low- and high-molecular-weight (HMW) proteinuria. Also, a shift in the distribution of lysosomes was seen in the XLAS dogs suggesting changes in the lysosomal degradation pattern in response to the altered endocytosis.
Conclusions: The present study shows that the increased glomerular permeability and the subsequently altered megalin-mediated and megalin-dependent cubilin-mediated endocytosis lead to a partial LMW proteinuria and partial HMW proteinuria.
Figures

References
-
- D'Amico G, Bazzi C. Pathophysiology of proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2003;63:809–825. - PubMed
-
- Maack T, Johnson V, Kau ST, et al. Renal filtration, transport, and metabolism of low-molecular-weight proteins: a review. Kidney Int. 1979;16:251–270. - PubMed
-
- Christensen EI, Nielsen R. Role of megalin and cubilin in renal physiology and pathophysiology. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2007;158:1–22. 1-22. - PubMed
-
- Christensen EI, Birn H. Multifunctional endocytic receptors. Nature reviews. 2002 - PubMed
-
- Birn H. The kidney in vitamin B12 and folate homeostasis: characterization of receptors for tubular uptake of vitamins and carrier proteins. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;291:F22–F36. - PubMed

