MISSA is a highly efficient in vivo DNA assembly method for plant multiple-gene transformation
- PMID: 20200068
- PMCID: PMC2862421
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.152249
MISSA is a highly efficient in vivo DNA assembly method for plant multiple-gene transformation
Abstract
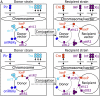
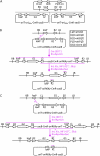
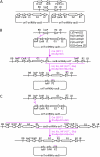
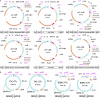
We describe a highly efficient in vivo DNA assembly method, multiple-round in vivo site-specific assembly (MISSA), which facilitates plant multiple-gene transformation. MISSA is based on conjugational transfer, which is driven by donor strains, and two in vivo site-specific recombination events, which are mediated by inducible Cre recombinase and phage lambda site-specific recombination proteins in recipient strains, to enable in vivo transfer and in vivo assembly of multiple transgenic DNA. The assembly reactions can be performed circularly and iteratively through alternate use of the two specially designed donor vectors. As proof-of-principle experiments, we constructed a few plant multigene binary vectors. One of these vectors was generated by 15 rounds of MISSA reactions and was confirmed in transgenic Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana). As MISSA simplifies the tedious and time-consuming in vitro manipulations to a simple mixing of bacterial strains, it will greatly save time, effort, and expense associated with the assembly of multiple transgenic or synthetic DNA. The principle that underlies MISSA is applicable to engineering polygenic traits, biosynthetic pathways, or protein complexes in all organisms, such as Escherichia coli, yeast, plants, and animals. MISSA also has potential applications in synthetic biology, whether for basic theory or for applied biotechnology, aiming at the assembly of genetic pathways for the production of biofuels, pharmaceuticals, and industrial compounds from natural or synthetic DNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delivery of multiple transgenes to plant cells by an improved version of MultiRound Gateway technology.Transgenic Res. 2013 Feb;22(1):153-67. doi: 10.1007/s11248-012-9640-0. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Transgenic Res. 2013. PMID: 22972476
-
MISSA 2.0: an updated synthetic biology toolbox for assembly of orthogonal CRISPR/Cas systems.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 3;7:41993. doi: 10.1038/srep41993. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28155921 Free PMC article.
-
High frequency of single-copy T-DNA transformants produced by floral dip in CRE-expressing Arabidopsis plants.Plant J. 2009 Aug;59(4):517-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03889.x. Epub 2009 Apr 6. Plant J. 2009. PMID: 19392707
-
Engineering crops, a deserving venture.Riv Biol. 2003 Jan-Apr;96(1):31-54. Riv Biol. 2003. PMID: 12852173 Review.
-
Higher plant transformation: principles and molecular tools.Int J Dev Biol. 2013;57(6-8):483-94. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.130232mv. Int J Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 24166431 Review.
Cited by
-
Co-expression of the Arabidopsis SOS genes enhances salt tolerance in transgenic tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.).Protoplasma. 2014 Jan;251(1):219-31. doi: 10.1007/s00709-013-0540-9. Protoplasma. 2014. PMID: 24022678 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Synthetic Metabolic Engineering for Enhancing Crop Nutritional Quality.Plant Commun. 2019 Dec 24;1(1):100017. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2019.100017. eCollection 2020 Jan 13. Plant Commun. 2019. PMID: 33404538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Delivery of multiple transgenes to plant cells by an improved version of MultiRound Gateway technology.Transgenic Res. 2013 Feb;22(1):153-67. doi: 10.1007/s11248-012-9640-0. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Transgenic Res. 2013. PMID: 22972476
-
Co-overexpression of the Constitutively Active Form of OsbZIP46 and ABA-Activated Protein Kinase SAPK6 Improves Drought and Temperature Stress Resistance in Rice.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jun 26;8:1102. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01102. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28694815 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering crassulacean acid metabolism to improve water-use efficiency.Trends Plant Sci. 2014 May;19(5):327-38. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.01.006. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Trends Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24559590 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexeyev MF, Shokolenko IN. (1995) RP4 oriT and RP4 oriT-R6K oriV DNA cassettes for construction of specialized vectors. Biotechniques 19: 22–24, 26 - PubMed
-
- Allen GC, Spiker S, Thompson WF. (2000) Use of matrix attachment regions (MARs) to minimize transgene silencing. Plant Mol Biol 43: 361–376 - PubMed
-
- An R, Chen QJ, Chai MF, Lu PL, Su Z, Qin ZX, Chen J, Wang XC. (2007) AtNHX8, a member of the monovalent cation:proton antiporter-1 family in Arabidopsis thaliana, encodes a putative Li/H antiporter. Plant J 49: 718–728 - PubMed
-
- Bernard P, Gabant P, Bahassi EM, Couturier M. (1994) Positive-selection vectors using the F plasmid ccdB killer gene. Gene 148: 71–74 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

