Ethanol stabilizes the open state of single 5-hydroxytryptamine(3A)(QDA) receptors
- PMID: 20200118
- PMCID: PMC2879933
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.164863
Ethanol stabilizes the open state of single 5-hydroxytryptamine(3A)(QDA) receptors
Abstract
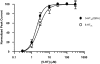
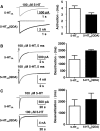
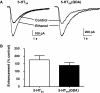
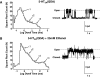
Ethanol enhancement of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)(3A) receptor-mediated responses may have important consequences in the intoxicating and addictive properties of ethanol. Although the exact mechanism is unknown, ethanol-mediated enhancement of 5-HT(3) receptor current has been proposed to occur due to stabilization of the open-channel state. It has not been possible to directly measure the open state of the channel due to the extremely low single-channel conductance of 5-HT(3A) channels. Recently, three arginine residues within the large intracellular loop of the 5-HT(3A) subunit were substituted by their equivalent residues (glutamine, aspartate, and alanine) of the 5-HT(3B) subunit to produce a 5-HT(3A)(QDA) subunit that forms functional homomeric channels exhibiting a measurable single-channel conductance. Using whole-cell rapid-agonist application techniques and the cell-attached single-channel recording configuration, we examined human 5-HT(3A)(QDA) receptors expressed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. The agonist sensitivity, macroscopic kinetics, and modulation by ethanol were similar between mutant and wild-type channels, suggesting the substitutions had not altered these channel structure-function properties. The open time histogram for single-channel events mediated by 5-HT(3A)(QDA) receptors in the presence of maximal 5-HT was best fit by three exponentials, but in the presence of ethanol a fourth open state was evident. In summary, the QDA substitution greatly enhanced single-channel conductance with little effect on 5-HT(3A) channel's kinetic properties and ethanol enhances agonist action on 5-HT(3A) receptors by inducing a new, long-lived open-channel state. Furthermore, the 5-HT(3A)(QDA) receptor appears to be suitable for pharmacological studies of 5-HT(3A) receptor modulation at a single-channel level.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Co-expression of the 5-HT(3B) subunit with the 5-HT(3A) receptor reduces alcohol sensitivity.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005 Dec 14;142(2):146-50. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.09.011. Epub 2005 Oct 28. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 16257471
-
General anesthetic-induced channel gating enhancement of 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 receptors depends on receptor subunit composition.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Nov;315(2):771-6. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.090621. Epub 2005 Aug 4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 16081679
-
Modular design of Cys-loop ligand-gated ion channels: functional 5-HT3 and GABA rho1 receptors lacking the large cytoplasmic M3M4 loop.J Gen Physiol. 2008 Feb;131(2):137-46. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709896. J Gen Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18227272 Free PMC article.
-
The 4'lysine in the putative channel lining domain affects desensitization but not the single-channel conductance of recombinant homomeric 5-HT3A receptors.J Physiol. 2000 Jan 15;522 Pt 2(Pt 2):187-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00187.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10639097 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the naturally occurring Arg344His variant of the human 5-HT 3A receptor.Pharmacol Rep. 2009 Sep-Oct;61(5):785-97. doi: 10.1016/s1734-1140(09)70134-3. Pharmacol Rep. 2009. PMID: 19904001
Cited by
-
Structure, Function and Physiology of 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptors Subtype 3.Subcell Biochem. 2021;96:373-408. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58971-4_11. Subcell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33252737 Review.
-
Alcohol-induced serotonergic modulation: the role of histone deacetylases.Alcohol. 2012 Nov;46(7):635-42. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2012.03.005. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Alcohol. 2012. PMID: 22796363 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric modulation of the 5-HT(3) receptor.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;11(1):75-80. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2011.01.010. Epub 2011 Feb 20. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21342788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline inhibits 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 receptor currents in NCB-20 cells.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;22(5):585-595. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.5.585. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30181705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borghese CM, Stórustovu S, Ebert B, Herd MB, Belelli D, Lambert JJ, Marshall G, Wafford KA, Harris RA. (2006) The delta subunit of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptors does not confer sensitivity to low concentrations of ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 316:1360–1368 - PubMed
-
- Campbell AD, Kohl RR, McBride WJ. (1996) Serotonin-3 receptor and ethanol-stimulated somatodendritic dopamine release. Alcohol 13:569–574 - PubMed
-
- Colquhoun D, Sigworth FJ. (1995) Fitting and statistical analysis of single-channel records, in Single-Channel Recording (Sakmann B, Neher E. eds) pp 483–587 Plenum, New York
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

