Cavitary pulmonary zygomycosis caused by Rhizopus homothallicus
- PMID: 20200286
- PMCID: PMC2863885
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01272-09
Cavitary pulmonary zygomycosis caused by Rhizopus homothallicus
Abstract
We report the first two proven cases of cavitary pulmonary zygomycosis caused by Rhizopus homothallicus. The diagnosis in each case was based on histology, culture of the causal agent, and the nucleotide sequence of the D1/D2 region of the 28S ribosomal DNA.
Figures

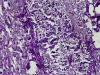
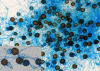
Similar articles
-
Fatal Pulmonary Mucormycosis due to Rhizopus homothallicus.Mycopathologia. 2017 Oct;182(9-10):907-913. doi: 10.1007/s11046-017-0151-7. Epub 2017 Jun 3. Mycopathologia. 2017. PMID: 28580534
-
Zygomycosis caused by Rhizopus microsporus and Rhizopus oryzae in Madhya Pradesh (M.P.) Central India: a report of two cases.Mycopathologia. 2012 Aug;174(2):171-6. doi: 10.1007/s11046-012-9532-0. Epub 2012 Mar 23. Mycopathologia. 2012. PMID: 22437261
-
Successful management of rhinosinusal zygomycosis in a renal transplant recipient.Mycoses. 2011 Sep;54(5):e593-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2010.01895.x. Epub 2010 May 26. Mycoses. 2011. PMID: 20524984 No abstract available.
-
Zygomycosis--a case report and overview of the disease in India.Mycoses. 2007 Jul;50(4):247-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2007.01382.x. Mycoses. 2007. PMID: 17576314 Review.
-
Chapter 7: zygomycosis.J Bras Pneumol. 2010 Jan-Feb;36(1):134-41. doi: 10.1590/s1806-37132010000100018. J Bras Pneumol. 2010. PMID: 20209316 Review. English, Portuguese.
Cited by
-
The impact of SARS-CoV-2 on the sudden onset of Mucormycosis in the Indian subcontinent-A review.J Family Med Prim Care. 2022 Aug;11(8):4246-4254. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_2244_21. Epub 2022 Aug 30. J Family Med Prim Care. 2022. PMID: 36352915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhizopus homothallicus, an emerging pathogen causing cavitary lung lesions.Access Microbiol. 2023 Apr 21;5(4):acmi000526.v3. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000526.v3. eCollection 2023. Access Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37223060 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptation to thermotolerance in Rhizopus coincides with virulence as revealed by avian and invertebrate infection models, phylogeny, physiological and metabolic flexibility.Virulence. 2015;6(4):395-403. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2015.1029219. Virulence. 2015. PMID: 26065324 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and Diagnosis of Mucormycosis: An Update.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Nov 2;6(4):265. doi: 10.3390/jof6040265. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33147877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of environmental Mucorales contamination in and around the residence of COVID-19-associated mucormycosis patients.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Sep 2;12:953750. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.953750. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36118044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe, A., Y. Oda, K. Asano, and T. Sone. 2006. The molecular phylogeny of genus Rhizopus based on rDNA sequences. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 70:2387-2393. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti, A., A. Das, A. Sharma, N. Panda, S. Das, K. L. Gupta, and V. Sakhuja. 2001. Ten years' experience in zygomycosis at a tertiary care centre in India. J. Infect. 42:261-266. - PubMed
-
- Chakrabarti, A., A. Das, J. Mandal, M. R. Shivprakash, V. K. George, B. Tarai, P. Rao, N. Panda, S. C. Verma, and V. Sakhuja. 2006. The rising trend of invasive zygomycosis in patients with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Med. Mycol. 44:335-342. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2002. Reference method for broth dilution susceptibility testing of filamentous fungi: approved standard M-38A. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

