Family-based analysis of candidate genes for polycystic ovary syndrome
- PMID: 20200332
- PMCID: PMC2869537
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2009-2703
Family-based analysis of candidate genes for polycystic ovary syndrome
Abstract
Context: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a complex disorder having both genetic and environmental components. A number of association studies based on candidate genes have reported significant association, but few have been replicated. D19S884, a polymorphic marker in fibrillin 3 (FBN3), is one of the few association findings that has been replicated in independent sets of families.
Objective: The aims of the study are: 1) to genotype single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the region of D19S884; and 2) to follow up with an independent data set, published results reporting evidence for PCOS candidate gene associations.
Design: The transmission disequilibrium test (TDT) was used to analyze linkage and association between PCOS and SNPs in candidate genes previously reported by us and by others as significantly associated with PCOS.
Setting: The study was conducted at academic medical centers.
Patients or other participants: A total of 453 families having a proband with PCOS participated in the study. Sisters with PCOS were also included. There was a total of 502 probands and sisters with PCOS.
Intervention(s): There were no interventions.
Main outcome measure(s): The outcome measure was transmission frequency of SNP alleles.
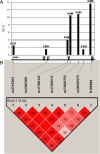
Results: We identified a six-SNP haplotype block spanning a 6.7-kb region on chromosome 19p13.2 that includes D19S884. SNP haplotype allele-C alone and in combination with D19S884-allele 8 is significantly associated with PCOS: haplotype-C TDT chi(2) = 10.0 (P = 0.0016) and haplotype-C/A8 TDT chi(2) = 7.6 (P = 0.006). SNPs in four of the other 26 putative candidate genes that were tested using the TDT were nominally significant (ACVR2A, POMC, FEM1B, and SGTA). One SNP in POMC (rs12473543, chi(2) = 9.1; P(corrected) = 0.042) is significant after correction for multiple testing.
Conclusions: A polymorphic variant, D19S884, in FBN3 is associated with risk of PCOS. POMC is also a candidate gene of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Is there a genetic basis for polycystic ovary syndrome?J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 May;95(5):2058-60. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0518. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20444933 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ehrmann DA 2005 Polycystic ovary syndrome. N Engl J Med 352:1223–1236 - PubMed
-
- Sam S, Dunaif A 2003 Polycystic ovary syndrome: syndrome XX? Trends Endocrinol Metab 14:365–370 - PubMed
-
- Menke MN, Strauss 3rd JF 2007 Genetic approaches to polycystic ovarian syndrome. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 19:355–359 - PubMed
-
- Urbanek M 2007 The genetics of the polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 3:103–111 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR010732/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR016499/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD034449/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD057450/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025741/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR10732/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000048/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR002635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR02635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD044405/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD033852/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HD033852/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD44405/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RR10732/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5R01HD058300/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD058300/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00048/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD34449/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

