A polymorphism in the VKORC1 regulator calumenin predicts higher warfarin dose requirements in African Americans
- PMID: 20200517
- PMCID: PMC2928561
- DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2009.291
A polymorphism in the VKORC1 regulator calumenin predicts higher warfarin dose requirements in African Americans
Abstract
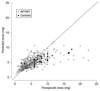
Warfarin demonstrates a wide interindividual variability in response that is mediated partly by variants in cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) and vitamin K 2,3-epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 (VKORC1). It is not known whether variants in calumenin (CALU) (vitamin K reductase regulator) have an influence on warfarin dose requirements. We resequenced CALU regions in a discovery cohort of dose outliers: patients with high (>90th percentile, n = 55) or low (<10th percentile, n = 53) warfarin dose requirements (after accounting for known genetic and nongenetic variables). One CALU variant, rs339097, was associated with high doses (P = 0.01). We validated this variant as a predictor of higher warfarin doses in two replication cohorts: (i) 496 patients of mixed ethnicity and (ii) 194 African-American patients. The G allele of rs339097 (the allele frequency was 0.14 in African Americans and 0.002 in Caucasians) was associated with the requirement for a 14.5% (SD +/- 7%) higher therapeutic dose (P = 0.03) in the first replication cohort and a higher-than-predicted dose in the second replication cohort (allele frequency 0.14, one-sided P = 0.03). CALU rs339097 A>G is associated with higher warfarin dose requirements, independent of known genetic and nongenetic predictors of warfarin dose in African Americans.
Conflict of interest statement
Washington University in St. Louis may file for a patent for CALU rs339097.
Figures

Similar articles
-
New genetic variant that might improve warfarin dose prediction in African Americans.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Sep;70(3):393-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2010.03709.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20716240 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and nongenetic factors associated with warfarin dose requirements in Egyptian patients.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2011 Mar;21(3):130-5. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0b013e3283436b86. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2011. PMID: 21228733 Free PMC article.
-
Factors influencing warfarin dose requirements in African-Americans.Pharmacogenomics. 2007 Nov;8(11):1535-44. doi: 10.2217/14622416.8.11.1535. Pharmacogenomics. 2007. PMID: 18034618 Clinical Trial.
-
The future of warfarin pharmacogenetics in under-represented minority groups.Future Cardiol. 2012 Jul;8(4):563-76. doi: 10.2217/fca.12.31. Future Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22871196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Warfarin sensitivity genotyping: a review of the literature and summary of patient experience.Mayo Clin Proc. 2009 Dec;84(12):1079-94. doi: 10.4065/mcp.2009.0278. Mayo Clin Proc. 2009. PMID: 19955245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fibulin-1C, C1 Esterase Inhibitor and Glucose Regulated Protein 75 Interact with the CREC Proteins, Calumenin and Reticulocalbin.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 10;10(7):e0132283. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132283. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26161649 Free PMC article.
-
Copy number variation and warfarin dosing: evaluation of CYP2C9, VKORC1, CYP4F2, GGCX and CALU.Pharmacogenomics. 2012 Feb;13(3):297-307. doi: 10.2217/pgs.11.156. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Pharmacogenomics. 2012. PMID: 22188360 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacogenomics of warfarin in populations of African descent.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;75(2):334-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04354.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22676711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic variant in folate homeostasis is associated with lower warfarin dose in African Americans.Blood. 2014 Oct 2;124(14):2298-305. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-568436. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Blood. 2014. PMID: 25079360 Free PMC article.
-
Clopidogrel and warfarin pharmacogenetic tests: what is the evidence for use in clinical practice?Curr Opin Cardiol. 2013 May;28(3):305-14. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0b013e32835f0bbc. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23478884 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Oden A, Fahlen M, Hart RG. Optimal INR for prevention of stroke and death in atrial fibrillation: a critical appraisal. Thromb Res. 2006;117:493–499. - PubMed
-
- Rieder MJ, Reiner AP, Gage BF, Nickerson DA, Eby CS, McLeod HL, et al. Effect of VKORC1 haplotypes on transcriptional regulation and warfarin dose. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:2285–2293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

