Cutaneous vaccination using microneedles coated with hepatitis C DNA vaccine
- PMID: 20200562
- PMCID: PMC2914565
- DOI: 10.1038/gt.2010.22
Cutaneous vaccination using microneedles coated with hepatitis C DNA vaccine
Abstract
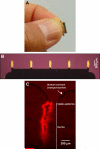
The skin is potentially an excellent organ for vaccine delivery because of accessibility and the presence of immune cells. However, no simple and inexpensive cutaneous vaccination method is available. Micron-scale needles coated with DNA were tested as a simple, inexpensive device for skin delivery. Vaccination with a plasmid encoding hepatitis C virus nonstructural 3/4A protein using microneedles effectively primed specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Importantly, the minimally invasive microneedles were as efficient in priming CTLs as more complicated or invasive delivery techniques, such as gene gun and hypodermic needles. Thus, microneedles may offer a promising technology for DNA vaccination.
Figures
Similar articles
-
In vivo clearance of hepatitis C virus nonstructural 3/4A-expressing hepatocytes by DNA vaccine-primed cytotoxic T lymphocytes.J Infect Dis. 2005 Dec 15;192(12):2112-6. doi: 10.1086/498218. Epub 2005 Nov 4. J Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16288375
-
Codon optimization and mRNA amplification effectively enhances the immunogenicity of the hepatitis C virus nonstructural 3/4A gene.Gene Ther. 2004 Mar;11(6):522-33. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3302184. Gene Ther. 2004. PMID: 14999224
-
Effective humoral immune response from a H1N1 DNA vaccine delivered to the skin by microneedles coated with PLGA-based cationic nanoparticles.J Control Release. 2017 Nov 10;265:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.04.027. Epub 2017 Apr 20. J Control Release. 2017. PMID: 28434892
-
Microneedle-based vaccines.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009;333:369-93. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-92165-3_18. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19768415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revealing the potential of DNA-based vaccination: lessons learned from the hepatitis B virus surface antigen.Biol Chem. 2001 Apr;382(4):543-52. doi: 10.1515/BC.2001.068. Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11405219 Review.
Cited by
-
Microneedle-based drug and vaccine delivery via nanoporous microneedle arrays.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015 Aug;5(4):397-406. doi: 10.1007/s13346-015-0238-y. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2015. PMID: 26044672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in microneedle array patch (MAP) for vaccine delivery.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021 Jan 2;17(1):316-327. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2020.1767997. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2021. PMID: 32667239 Free PMC article.
-
Simple and customizable method for fabrication of high-aspect ratio microneedle molds using low-cost 3D printing.Microsyst Nanoeng. 2019 Sep 9;5:42. doi: 10.1038/s41378-019-0088-8. eCollection 2019. Microsyst Nanoeng. 2019. PMID: 31645996 Free PMC article.
-
Microneedle-based intradermal delivery of stabilized dengue virus.Bioeng Transl Med. 2019 Feb 25;4(2):e10127. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10127. eCollection 2019 May. Bioeng Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31249877 Free PMC article.
-
Coating solid dispersions on microneedles via a molten dip-coating method: development and in vitro evaluation for transdermal delivery of a water-insoluble drug.J Pharm Sci. 2014 Nov;103(11):3621-3630. doi: 10.1002/jps.24159. Epub 2014 Sep 11. J Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 25213295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Garmory HS, Perkins SD, Phillpotts RJ, Titball RW. DNA vaccines for biodefence. Adv Drug Deliver Rev. 2005;57:1343–1361. - PubMed
-
- Donnelly J, Berry K, Ulmer JB. Technical and regulatory hurdles for DNA vaccines. Int J Parasitol. 2003;33:457–467. - PubMed
-
- Nicolas JF, Guy B. Intradermal, epidermal and transcutaneous vaccination: from immunology to clinical practice. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2008;7:1201–1214. - PubMed
-
- Prausnitz MR, Mikszta JA, Cormier M, Andrianov AK. Microneedle-based vaccines. In: Compans RW, Orenstein WA, editors. Current Topics in Microbiology & Immunology: Vaccines for Pandemic Influenza. Springer-Verlag; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2009.
-
- Matriano JA, Cormier M, Johnson J, Young WA, Buttery M, Nyam K, et al. Macroflux microprojection array patch technology: a new and efficient approach for intracutaneous immunization. Pharm Res. 2002;19:63–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

