Smurf1 inhibits mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation into osteoblasts through JunB degradation
- PMID: 20200942
- PMCID: PMC3153132
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.28
Smurf1 inhibits mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and differentiation into osteoblasts through JunB degradation
Abstract
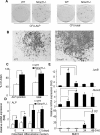
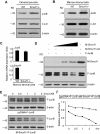
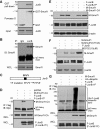
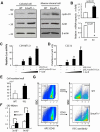
Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1-deficient mice develop an increased-bone-mass phenotype in an age-dependent manner. It was reported that such a bone-mass increase is related to enhanced activities of differentiated osteoblasts. Although osteoblasts are of mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) origin and MSC proliferation and differentiation can have significant impacts on bone formation, it remains largely unknown whether regulation of MSCs plays a role in the bone-mass increase of Smurf1-deficient mice. In this study we found that bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells from Smurf1(-/-) mice form significantly increased alkaline phosphatase-positive colonies, indicating roles of MSC proliferation and differentiation in bone-mass accrual of Smurf1(-/-) mice. Interestingly, Smurf1(-/-) cells have an elevated protein level of AP-1 transcription factor JunB. Biochemical experiments demonstrate that Smurf1 interacts with JunB through the PY motif and targets JunB protein for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Indeed, Smurf1-deficient MSCs have higher proliferation rates, consistent with the facts that cyclin D1 mRNA and protein both are increased in Smurf1(-/-) cells and JunB can induce cyclinD1 promoter. Moreover, JunB overexpression induces osteoblast differentiation, shown by higher expression of osteoblast markers, and JunB knock-down not only decreases osteoblast differentiation but also restores the osteogenic potential to wild-type level in Smurf1(-/-) cells. In conclusion, our results suggest that Smurf1 negatively regulates MSC proliferation and differentiation by controlling JunB turnover through an ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
(c) 2010 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tumor necrosis factor inhibits mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts via the ubiquitin E3 ligase Wwp1.Stem Cells. 2011 Oct;29(10):1601-10. doi: 10.1002/stem.703. Stem Cells. 2011. PMID: 21809421 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin E3 ligase Wwp1 negatively regulates osteoblast function by inhibiting osteoblast differentiation and migration.J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Sep;28(9):1925-35. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1938. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 23553732 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin e3 ligase itch negatively regulates osteoblast differentiation from mesenchymal progenitor cells.Stem Cells. 2013 Aug;31(8):1574-83. doi: 10.1002/stem.1395. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23606569 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Roles of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases and Deubiquitinases in Bone.Biomolecules. 2025 May 7;15(5):679. doi: 10.3390/biom15050679. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40427572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adult mesenchymal stem cells: is there a role for purine receptors in their osteogenic differentiation?Purinergic Signal. 2020 Sep;16(3):263-287. doi: 10.1007/s11302-020-09703-4. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Purinergic Signal. 2020. PMID: 32500422 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NEDD4 E3 Ligases: Functions and Mechanisms in Bone and Tooth.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 1;23(17):9937. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179937. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-Wide CRISPR/Cas9-Based Screening for Deubiquitinase Subfamily Identifies Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 11 as a Novel Regulator of Osteogenic Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 13;23(2):856. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020856. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35055037 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of RNAi-Based Therapeutics for Bone Regeneration.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020 Jun;18(3):312-324. doi: 10.1007/s11914-020-00587-2. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2020. PMID: 32394316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutually exclusive acetylation and ubiquitylation of the splicing factor SRSF5 control tumor growth.Nat Commun. 2018 Jun 25;9(1):2464. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04815-3. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29942010 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin E3 ligase Itch negatively regulates osteoblast function by promoting proteasome degradation of osteogenic proteins.Bone Joint Res. 2017 Mar;6(3):154-161. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.63.BJR-2016-0237.R1. Bone Joint Res. 2017. PMID: 28298321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karsenty G, Wagner EF. Reaching a genetic and molecular understanding of skeletal development. Dev Cell. 2002;2:389–406. - PubMed
-
- Ducy P, Zhang R, Geoffroy V, Ridall AL, Karsenty G. Osf2/Cbfa1: a transcriptional activator of osteoblast differentiation. Cell. 1997;89:747–754. - PubMed
-
- Komori Y, Yagi H, Nomura S, et al. Targeted disruption of Cbfa 1 results in a complete lack of bone formation owing to maturational arrest of osteoblasts. Cell. 1997;89:755–764. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H, Kavsak P, Abdollah S, Wrana JL, Thomsen GH. A SMAD ubiquitin ligase targets the BMP pathway and affects embryonic pattern formation. Nature. 1999;400:687–693. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

