Correlates of trabecular and cortical volumetric bone mineral density of the radius and tibia in older men: the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study
- PMID: 20200975
- PMCID: PMC3153367
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.6
Correlates of trabecular and cortical volumetric bone mineral density of the radius and tibia in older men: the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study
Abstract
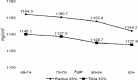
Quantitative computed tomography (QCT) can estimate volumetric bone mineral density (vBMD) and distinguish trabecular from cortical bone. Few comprehensive studies have examined correlates of vBMD in older men. This study evaluated the impact of demographic, anthropometric, lifestyle, and medical factors on vBMD in 1172 men aged 69 to 97 years and enrolled in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men Study (MrOS). Peripheral quantitative computed tomography (pQCT) was used to measure vBMD of the radius and tibia. The multivariable linear regression models explained up to 10% of the variance in trabecular vBMD and up to 9% of the variance in cortical vBMD. Age was not correlated with radial trabecular vBMD. Correlates associated with both cortical and trabecular vBMD were age (-), caffeine intake (-), total calcium intake (+), nontrauma fracture (-), and hypertension (+). Higher body weight was related to greater trabecular vBMD and lower cortical vBMD. Height (-), education (+), diabetes with thiazolidinedione (TZD) use (+), rheumatoid arthritis (+), using arms to stand from a chair (-), and antiandrogen use (-) were associated only with trabecular vBMD. Factors associated only with cortical vBMD included clinic site (-), androgen use (+), grip strength (+), past smoker (-), and time to complete five chair stands (-). Certain correlates of trabecular and cortical vBMD differed among older men. An ascertainment of potential risk factors associated with trabecular and cortical vBMD may lead to better understanding and preventive efforts for osteoporosis in men.
(c) 2010 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Figures
References
-
- Cauley JA, Fullman RL, Stone KL, et al. Factors associated with the lumbar spine and proximal femur bone mineral density in older men. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16:1525–1537. - PubMed
-
- Melton LJ, III, Chrischilles EA, Cooper C, Lane AW, Riggs BL. How many women have osteoporosis? JBMR Anniversary Classic. J Bone Miner Res. 1992;7 J Bone Miner Res. 2005;20:886–892. - PubMed
-
- Natsui K, Tanaka K, Suda M, et al. High-dose glucocorticoid treatment induces rapid loss of trabecular bone mineral density and lean body mass. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17:105–108. - PubMed
-
- Seeman E. From density to structure: growing up and growing old on the surfaces of bone. J Bone Miner Res. 1997;12:509–521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AR45632/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG024827/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45647/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45614/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045614/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45654/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045654/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042140/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45583/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045647/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR45580/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG027810/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024140/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045580/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG18197/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG018197/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR066160/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR045632/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous