Genetic deficiency of Syk protects mice from autoantibody-induced arthritis
- PMID: 20201079
- PMCID: PMC2972644
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27438
Genetic deficiency of Syk protects mice from autoantibody-induced arthritis
Abstract
Objective: The Syk tyrosine kinase plays an important role in diverse functions in hematopoietic lineage cells. Although previous in vitro and pharmacologic analyses suggested Syk to be a possible player in the development of autoimmune arthritis, no in vivo genetic studies addressing that issue have yet been reported. The aim of the present study was to test whether genetic deficiency of Syk affects autoantibody-induced experimental arthritis in the K/BxN serum-transfer model.
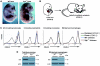
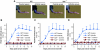
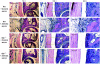
Methods: Syk(-/-) bone marrow chimeras carrying a Syk-deficient hematopoietic system were generated by transplanting Syk(-/-) fetal liver cells into lethally irradiated wild-type recipients. After complete repopulation of the hematopoietic compartment, autoantibody-mediated arthritis was induced by injection of arthritogenic K/BxN serum. Arthritis development was monitored by macroscopic and microscopic observation of the ankle joints, micro-computed tomography of bone morphology, as well as a joint function assay.
Results: Genetic deficiency of Syk in the hematopoietic compartment completely blocked the development of all macroscopic and microscopic signs of arthritis. The Syk(-/-) mutation also prevented the appearance of periarticular bone erosions. Finally, Syk(-/-) bone marrow chimeras were completely protected from arthritis-induced loss of articular function.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that Syk is critically involved in the development of all clinically relevant aspects of autoantibody-mediated K/BxN serum-transfer arthritis in experimental mice. These results provide the first in vivo genetic evidence of the role of Syk in the development of autoimmune arthritis.
Figures
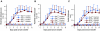

Similar articles
-
Lineage-Specific Analysis of Syk Function in Autoantibody-Induced Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 19;9:555. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00555. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29616043 Free PMC article.
-
Syk-dependent signaling pathways in neutrophils and macrophages are indispensable in the pathogenesis of anti-collagen antibody-induced arthritis.Int Immunol. 2012 Sep;24(9):539-50. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxs078. Int Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22914861
-
Critical role of phospholipase Cgamma2 in integrin and Fc receptor-mediated neutrophil functions and the effector phase of autoimmune arthritis.J Exp Med. 2009 Mar 16;206(3):577-93. doi: 10.1084/jem.20081859. Epub 2009 Mar 9. J Exp Med. 2009. PMID: 19273622 Free PMC article.
-
[Involvement of Syk in pathology of systemic autoimmune disease].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2012;35(1):56-61. doi: 10.2177/jsci.35.56. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2012. PMID: 22374444 Review. Japanese.
-
The role and clinical implications of G6PI in experimental models of rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7(1):20-8. doi: 10.1186/ar1476. Epub 2004 Nov 30. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005. PMID: 15642150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling through Syk or CARD9 Mediates Species-Specific Anti-Candida Protection in Bone Marrow Chimeric Mice.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0160821. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01608-21. Epub 2021 Aug 31. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34465030 Free PMC article.
-
PRT062607 Achieves Complete Inhibition of the Spleen Tyrosine Kinase at Tolerated Exposures Following Oral Dosing in Healthy Volunteers.J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Feb;57(2):194-210. doi: 10.1002/jcph.794. Epub 2016 Aug 17. J Clin Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27406873 Free PMC article.
-
Microglial aryl hydrocarbon receptor enhances phagocytic function via SYK and promotes remyelination in the cuprizone mouse model of demyelination.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Mar 25;20(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02764-3. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 36966295 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in rheumatoid arthritis animal models.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2011 Oct;13(5):456-63. doi: 10.1007/s11926-011-0200-z. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21792748 Free PMC article.
-
Kinase inhibition in autoimmunity and inflammation.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021 Jan;20(1):39-63. doi: 10.1038/s41573-020-0082-8. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 33077936 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–61. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:429–42. - PubMed
-
- Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, et al. Efficacy of B-cell–targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2572–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

