Identification of a distant cis-regulatory element controlling pharyngeal arch-specific expression of zebrafish gdf6a/radar
- PMID: 20201106
- PMCID: PMC3110066
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.22251
Identification of a distant cis-regulatory element controlling pharyngeal arch-specific expression of zebrafish gdf6a/radar
Abstract
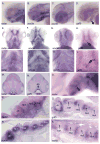
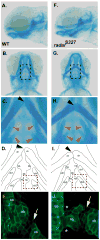
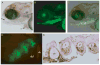
Skeletal formation is an essential and intricately regulated part of vertebrate development. Humans and mice deficient in growth and differentiation factor 6 (Gdf6) have numerous skeletal abnormalities, including joint fusions and cartilage reductions. The expression of Gdf6 is dynamic and in part regulated by distant evolutionarily conserved cis-regulatory elements. radar/gdf6a is a zebrafish ortholog of Gdf6 and has an essential role in embryonic patterning. Here, we show that radar is transcribed in the cells surrounding and between the developing cartilages of the ventral pharyngeal arches, similar to mouse Gdf6. A 312 bp evolutionarily conserved region (ECR5), 122 kilobases downstream, drives expression in a pharyngeal arch-specific manner similar to endogenous radar/gdf6a. Deletion analysis identified a 78 bp region within ECR5 that is essential for transgene activity. This work illustrates that radar is regulated in the pharyngeal arches by a distant conserved element and suggests radar has similar functions in skeletal development in fish and mammals.
Figures




References
-
- Angelo S, Lohr J, Lee KH, Ticho BS, Breitbart RE, Hill S, Yost HJ, Srivastava D. Conservation of sequence and expression of Xenopus and zebrafish dHAND during cardiac, branchial arch and lateral mesoderm development. Mech Dev. 2000;95:231–237. - PubMed
-
- Asai-Coakwell M, French CR, Ye M, Garcha K, Bigot K, Perera AG, Staehling-Hampton K, Mema SC, Chanda B, Mushegian A, Bamforth S, Doschak MR, Li G, Dobbs MB, Giampietro PF, Brooks BP, Vijayalakshmi P, Sauve Y, Abitbol M, Sundaresan P, Heyningen VV, Pourquie O, Underhill TM, Waskiewicz AJ, Lehmann OJ. Incomplete penetrance and phenotypic variability characterize Gdf6-attributable oculo-skeletal phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet. 2009;18:1110–1121. - PubMed
-
- Bruneau S, Mourrain P, Rosa FM. Expression of contact, a new zebrafish DVR member, marks mesenchymal cell lineages in the developing pectoral fins and head and is regulated by retinoic acid. Mech Dev. 1997;65:163–173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

