DNA damage intensity in fibroblasts in a 3-dimensional collagen matrix correlates with the Bragg curve energy distribution of a high LET particle
- PMID: 20201648
- PMCID: PMC3382085
- DOI: 10.3109/09553000903418603
DNA damage intensity in fibroblasts in a 3-dimensional collagen matrix correlates with the Bragg curve energy distribution of a high LET particle
Abstract
Purpose: The DNA double-strand break (DSB) damage response induced by high energy charged particles on lung fibroblast cells embedded in a 3-dimensional (3-D) collagen tissue equivalents was investigated using antibodies to the DNA damage response proteins gamma-histone 2AX (gamma-H2AX) and phosphorylated DNA-PKcs (p-DNA-PKcs).
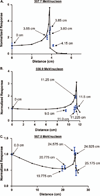
Materials and methods: 3-D tissue equivalents were irradiated in positions across the linear distribution of the Bragg curve profiles of 307.7 MeV/nucleon, 556.9 MeV/nucleon, or 967.0 MeV/nucleon (56)Fe ions at a dose of 0.30 Gy.
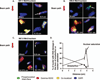
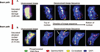
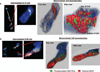
Results: Patterns of discrete DNA damage streaks across nuclei or saturated nuclear damage were observed, with saturated nuclear damage being more predominant as samples were positioned closer to the physical Bragg peak. Quantification of the DNA damage signal intensities at each distance for each of the examined energies revealed a biological Bragg curve profile with a pattern of DNA damage intensity similar to the physical Bragg curve for the particular energy. Deconvolution microscopy of nuclei with streaked or saturated nuclear damage pattern revealed more details of the damage, with evidence of double-strand breaks radially distributed from the main particle track as well as multiple discrete tracks within saturated damage nuclei.
Conclusions: These 3-D culture systems can be used as a biological substrate to better understand the interaction of heavy charged particles of different energies with tissue and could serve as a basis to model space-radiation-induced cancer initiation and progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Asaithamby A, Uematsu N, Chatterjee A, Story MD, Burma S, Chen DJ. Repair of HZE-particle-induced DNA double-strand breaks in normal human fibroblasts. Radiation Research. 2008;169:437–446. - PubMed
-
- Chen BP, Chan DW, Kobayashi J, Burma S, Asaithamby A, Morotomi-Yano K, Botvinick E, Qin J, Chen DJ. Cell cycle dependence of DNA-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation in response to DNA double strand breaks. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2005;280:14709–14715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
