Akt inhibition up-regulates MMP1 through a CCN2-dependent pathway in human dermal fibroblasts
- PMID: 20201953
- PMCID: PMC3826663
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2010.01065.x
Akt inhibition up-regulates MMP1 through a CCN2-dependent pathway in human dermal fibroblasts
Abstract
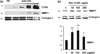
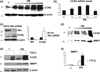
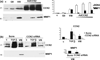
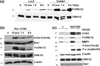
Akt is a key signalling molecule that was found to be down-regulated in chronic wounds. Akt blockade has dual antifibrotic effects in human dermal fibroblasts, by up-regulating matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) and down-regulating collagen gene expression (J Invest Dermatol 2008: 128: 1906). The aim of this study was to gain additional insights into the mechanism of MMP1 up-regulation following Akt blockade. As previous studies showed that CCN2 can be a positive regulator of MMP1, we examined the effects of Akt inhibition on CCN2 expression. Akt blockade using a specific pharmacological inhibitor and Akt siRNA resulted in a significant up-regulation of CCN2, which correlated with the increase in MMP1. The MMP1 up-regulation following Akt blockade was partially suppressed by CCN2 siRNA, suggesting that CCN2 is contributing to this effect. Additional experiments showed that CCN2 induces phosphorylation of ERK1/2, Ets1 and c-Jun. Consistent with the stimulatory role of ERK1/2/Ets1 in the expression of MMP1, the ERK1/2 inhibitor UO126 prevented the phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and Ets1 and completely abrogated the induction of MMP1 after CCN2 overexpression, while having no effect on c-Jun activation. Taken together these results establish CCN2 as a key regulator of MMP1 induction via activation of the ERK1/2/Ets1 pathway. Down-regulation of Akt signalling leads to inappropriate activation of the CCN2/MMP1 pathway that may contribute to the pathogenesis of chronic wounds. Coordinate expression of CCN2, Akt and MMP1 could be important for normal wound healing to occur. Thus, targeting these specific proteins may represent a promising approach to the therapy of dysregulated wound healing.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Caveolin-1 is a negative regulator of MMP-1 gene expression in human dermal fibroblasts via inhibition of Erk1/2/Ets1 signaling pathway.J Dermatol Sci. 2011 Dec;64(3):210-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Aug 30. J Dermatol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21925842 Free PMC article.
-
Akt blockade downregulates collagen and upregulates MMP1 in human dermal fibroblasts.J Invest Dermatol. 2008 Aug;128(8):1906-14. doi: 10.1038/jid.2008.39. Epub 2008 Mar 6. J Invest Dermatol. 2008. PMID: 18323784
-
Fli1 and Ets1 have distinct roles in connective tissue growth factor/CCN2 gene regulation and induction of the profibrotic gene program.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 1;281(35):25259-69. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M600466200. Epub 2006 Jul 6. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16829517
-
Ciprofloxacin has antifibrotic effects in scleroderma fibroblasts via downregulation of Dnmt1 and upregulation of Fli1.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Dec;30(6):1473-80. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1150. Epub 2012 Oct 5. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 23041765 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate stimulates MMP1 gene expression via activation of ERK1/2-Ets1 pathway in human fibroblasts.FASEB J. 2006 Jan;20(1):184-6. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-4646fje. Epub 2005 Nov 8. FASEB J. 2006. PMID: 16278291
Cited by
-
Caveolin-1 is a negative regulator of MMP-1 gene expression in human dermal fibroblasts via inhibition of Erk1/2/Ets1 signaling pathway.J Dermatol Sci. 2011 Dec;64(3):210-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2011.08.005. Epub 2011 Aug 30. J Dermatol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21925842 Free PMC article.
-
Thymosin beta-4 improves endothelial function and reparative potency of diabetic endothelial cells differentiated from patient induced pluripotent stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jan 10;13(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02687-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35012642 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative and pharmacological investigation of bEVs from eight Lactobacillales strains.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 26;15(1):27263. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12873-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40715596 Free PMC article.
-
The c-Abl tyrosine kinase controls protein kinase Cδ-induced Fli-1 phosphorylation in human dermal fibroblasts.Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Jun;63(6):1729-37. doi: 10.1002/art.30284. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21321929 Free PMC article.
-
Network medicine based approach for identifying the type 2 diabetes, osteoarthritis and triple negative breast cancer interactome: Finding the hub of hub genes.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 22;10(17):e36650. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36650. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39281650 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Werner S, Grose R. Regulation of wound healing by growth factors and cytokines. Physiol Rev. 2003;83:835–870. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal S, Achari C, Praveen D, Roy KR, Reddy GV, Reddanna P. Inhibition of 12-LOX and COX-2 reduces the proliferation of human epidermoid carcinoma cells (A431) by modulating the ERK and PI3K-Akt signalling pathways. Exp Dermatol. 2009;18:939–946. - PubMed
-
- Kim D, Chung J. Akt: versatile mediator of cell survival and beyond. J Biochem Mol Biol. 2002;35:106–115. - PubMed
-
- Aarabi S, Bhatt KA, Shi Y, et al. Mechanical load initiates hypertrophic scar formation through decreased cellular apoptosis. FASEB J. 2007;21:3250–3261. - PubMed
-
- Goren I, Muller E, Schiefelbein D, et al. Akt1 controls insulin-driven VEGF biosynthesis from keratinocytes: implications for normal and diabetes-impaired skin repair in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:752–764. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

