Optimal stimulation for CD70 induction on human monocyte-derived dendritic cells and the importance of CD70 in naive CD4(+) T-cell differentiation
- PMID: 20201989
- PMCID: PMC2855801
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2010.03220.x
Optimal stimulation for CD70 induction on human monocyte-derived dendritic cells and the importance of CD70 in naive CD4(+) T-cell differentiation
Abstract
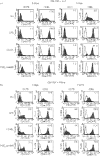
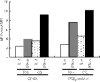
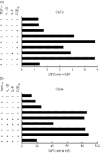
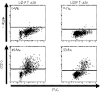
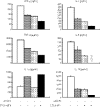
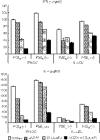
Studies in mice have shown that CD70 on dendritic cells (DCs) is sufficient to convert T-cell tolerance into immunity and hence induce anti-tumour immune responses. Therefore, it is important to investigate (i) optimal stimuli to induce CD70 on human monocyte-derived DCs (MoDCs), which are widely used for tumour immunotherapy, and (ii) the role of CD70 in functional differentiation of naive CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells stimulated with MoDCs. We show that interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) is a key cytokine to differentiate monocytes into DCs with the capacity to express CD70 upon maturation. CD70 expression on IFN-alpha-induced MoDCs was elicited by different categories of maturation-inducing factors (Toll-like receptor ligands, CD40 ligand and pro-inflammatory mediators), among which prostaglandin E(2) was most effective. Naive T cells stimulated with MoDCs also expressed CD70. Stimulation with MoDCs promoted naive CD4(+) T cells to acquire the ability to produce T helper type 1 and 2 cytokines in a CD70-dependent manner. In contrast, the CD70-CD27 interaction diminished the production of an immunoregulatory cytokine IL-10. The CD27 signal did not play a dominant role in the induction of effector molecules in naive CD8(+) T cells during the stimulation with MoDCs. This study adds a novel function to the versatile cytokines, type I IFNs, that is, the induction of CD70 on MoDCs. CD70 promotes naive CD4(+) T cells to acquire immunostimulatory activity through the DC-T-cell and T-cell-T-cell interactions during the stimulation with MoDCs. Hence, the CD70-CD27 interaction may play an important role in inducing effective immune responses in DC-based immunotherapy.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The CD70-CD27 interaction during the stimulation with dendritic cells promotes naive CD4(+) T cells to develop into T cells producing a broad array of immunostimulatory cytokines in humans.Int Immunol. 2009 Aug;21(8):891-904. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxp056. Epub 2009 Jun 25. Int Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19556308
-
Expression of costimulatory ligand CD70 on steady-state dendritic cells breaks CD8+ T cell tolerance and permits effective immunity.Immunity. 2008 Dec 19;29(6):934-46. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2008.10.009. Epub 2008 Dec 8. Immunity. 2008. PMID: 19062317
-
Human dendritic cells stimulated via TLR7 and/or TLR8 induce the sequential production of Il-10, IFN-gamma, and IL-17A by naive CD4+ T cells.J Immunol. 2009 Mar 15;182(6):3372-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0801969. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19265114
-
Differentiation and function of mouse monocyte-derived dendritic cells in steady state and inflammation.Immunol Rev. 2010 Mar;234(1):90-104. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2009.00876.x. Immunol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20193014 Review.
-
Interferon-α in the generation of monocyte-derived dendritic cells: recent advances and implications for dermatology.Br J Dermatol. 2011 Aug;165(2):247-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10301.x. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Br J Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21410666 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimizing dendritic cell-based immunotherapy: tackling the complexity of different arms of the immune system.Mediators Inflamm. 2012;2012:690643. doi: 10.1155/2012/690643. Epub 2012 Jul 18. Mediators Inflamm. 2012. PMID: 22851815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the Other Side: Manipulating the Immune Checkpoint Landscape of Dendritic Cells to Enhance Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Oncol. 2019 Feb 6;9:50. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00050. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30788290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interferon gamma licensing of human dendritic cells in T-helper-independent CD8+ alloimmunity.Blood. 2010 Oct 21;116(16):3089-98. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-02-268623. Epub 2010 Jul 19. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20644110 Free PMC article.
-
The dark side of dendritic cells: development and exploitation of tolerogenic activity that favor tumor outgrowth and immune escape.Front Immunol. 2013 Dec 2;4:419. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00419. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24348482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PTPN3 inhibition contributes to the activation of the dendritic cell function to be a promising new immunotherapy target.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(16):14619-14630. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05250-8. Epub 2023 Aug 16. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37584709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Watts TH. TNF/TNFR family members in costimulation of T cell responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:23–68. - PubMed
-
- Borst J, Hendriks J, Xiao Y. CD27 and CD70 in T cell and B cell activation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005;17:275–81. - PubMed
-
- Hendriks J, Gravestein LA, Tesselaar K, van Lier RAW, Schumacher TNM, Borst J. CD27 is required for generation and long-term maintenance of T cell immunity. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:433. - PubMed
-
- Arens R, Tesselaar K, Baars PA, et al. Constitutive CD27/CD70 interaction induces expansion of effector-type T cells and results in IFN-γ-mediated B cell depletion. Immunity. 2001;15:801. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

