Mycobacterium tuberculosis conserved hypothetical protein rRv2626c modulates macrophage effector functions
- PMID: 20201990
- PMCID: PMC2855791
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03196.x
Mycobacterium tuberculosis conserved hypothetical protein rRv2626c modulates macrophage effector functions
Abstract
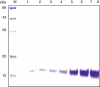
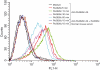
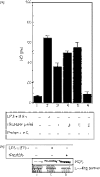
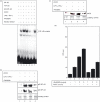
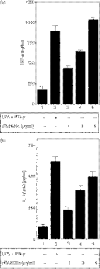
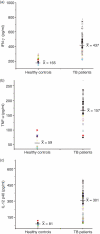
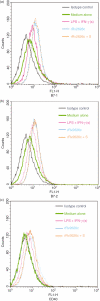
Secretory proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis are the major immunomodulators of the host immune response. Open reading frame (ORF) Rv2626c, encoding a conserved hypothetical protein eliciting a strong humoral immune response in patients with tuberculosis (TB), was shown to be up-regulated upon infection in mice under hypoxic conditions. We now show that recombinant Rv2626c protein (rRv2626c) can bind to the surface of murine macrophages and elicit the type-1 immune response, as manifested by nitric oxide (NO) secretion and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). Significant induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines [interleukin (IL)-12 and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha] was evident upon stimulation of murine macrophages, as well as peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) isolated from patients with active TB disease, with rRv2626c. Stimulation with rRv2626c also enhanced the expression of costimulatory molecules such as B7-1, B7-2 and CD40 on murine macrophages. We further show that the production of NO and pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to rRv2626c is mediated by the transcription factor nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB, and this was further confirmed using pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), a specific pharmacological inhibitor of NF-kappaB. Rv2626c therefore appears to modulate macrophage effector functions by eliciting both innate and adaptive immune responses, suggesting its possible use as a vaccine candidate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-inducible nitric oxide synthase and IL-1beta through suppression of NF-kappaB activation by 3-(1'-1'-dimethyl-allyl)-6-hydroxy-7-methoxy-coumarin isolated from Ruta graveolens L.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Mar 29;560(1):69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.01.002. Epub 2007 Jan 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17292351
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis hypoxic response protein 1 (Hrp1) augments the pro-inflammatory response and enhances the survival of Mycobacterium smegmatis in murine macrophages.J Med Microbiol. 2017 Jul;66(7):1033-1044. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000511. Epub 2017 Jul 31. J Med Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28671529
-
Frizzled1 is a marker of inflammatory macrophages, and its ligand Wnt3a is involved in reprogramming Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages.FASEB J. 2010 Nov;24(11):4599-612. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-160994. Epub 2010 Jul 28. FASEB J. 2010. PMID: 20667980
-
gp130 on macrophages/granulocytes modulates inflammation during experimental tuberculosis.Eur J Cell Biol. 2011 Jun-Jul;90(6-7):505-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2010.10.010. Epub 2010 Dec 8. Eur J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21144615 Review.
-
What is the role of nitric oxide in murine and human host defense against tuberculosis?Current knowledge.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001 Nov;25(5):606-12. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.25.5.4487. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11713103 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin 34 Serves as a Novel Molecular Adjuvant against Nocardia Seriolae Infection in Largemouth Bass (Micropterus Salmoides).Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Mar 28;8(2):151. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8020151. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32231137 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv2626c-derived peptide as a therapeutic agent for sepsis.EMBO Mol Med. 2020 Dec 7;12(12):e12497. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202012497. Epub 2020 Dec 1. EMBO Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33258196 Free PMC article.
-
Gene Regulatory Mechanism of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis during Dormancy.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Jun 11;46(6):5825-5844. doi: 10.3390/cimb46060348. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38921019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Commentary: Modification of Host Responses by Mycobacteria.Front Immunol. 2017 Apr 28;8:466. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00466. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28503174 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Turning a pathogen protein into a therapeutic tool for sepsis.EMBO Mol Med. 2021 Jan 11;13(1):e13589. doi: 10.15252/emmm.202013589. Epub 2020 Dec 17. EMBO Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 33332738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colditz GA, Brewer TF, Berkey CS, Wilson ME, Burdick E, Fineberg HV, Mosteller F. Efficacy of BCG vaccine in the prevention of tuberculosis. Meta-analysis of the published literature. JAMA. 1994;271:698–702. - PubMed
-
- Braun MM, Cauthen G. Relationship of the human immunodeficiency virus epidemic to pediatric tuberculosis and Bacillus Calmette-Guerin immunization. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1992;11:220–7. - PubMed
-
- von Reyn CF, Clements CJ, Mann JM. Human immunodeficiency virus infection and routine childhood immunisation. Lancet. 1987;19:669–72. - PubMed
-
- Weltman AC, Rose DN. The safety of Bacilli Calmette-Guerin vaccination in HIV infection and AIDS. AIDS. 1993;2:149–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

