Membrane attack complex inhibitor CD59a protects against focal cerebral ischemia in mice
- PMID: 20202211
- PMCID: PMC2839971
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-7-15
Membrane attack complex inhibitor CD59a protects against focal cerebral ischemia in mice
Abstract
Background: The complement system is a crucial mediator of inflammation and cell lysis after cerebral ischemia. However, there is little information about the exact contribution of the membrane attack complex (MAC) and its inhibitor-protein CD59.
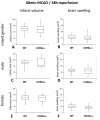
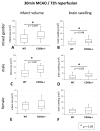
Methods: Transient focal cerebral ischemia was induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in young male and female CD59a knockout and wild-type mice. Two models of MCAO were applied: 60 min MCAO and 48 h reperfusion, as well as 30 min MCAO and 72 h reperfusion. CD59a knockout animals were compared to wild-type animals in terms of infarct size, edema, neurological deficit, and cell death.
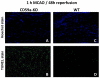
Results and discussion: CD59a-deficiency in male mice caused significantly increased infarct volumes and brain swelling when compared to wild-type mice at 72 h after 30 min-occlusion time, whereas no significant difference was observed after 1 h-MCAO. Moreover, CD59a-deficient mice had impaired neurological function when compared to wild-type mice after 30 min MCAO.
Conclusion: We conclude that CD59a protects against ischemic brain damage, but depending on the gender and the stroke model used.
Figures
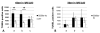

Similar articles
-
Brain infarct volume after permanent focal ischemia is not dependent on Nox2 expression.Brain Res. 2012 Nov 5;1483:105-11. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.09.023. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 23000198
-
Thalidomide protects against ischemic neuronal damage induced by focal cerebral ischemia in mice.Neuroscience. 2009 Mar 17;159(2):760-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.12.043. Epub 2009 Jan 1. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19166916
-
Tacrolimus (FK506) attenuates biphasic cytochrome c release and Bad phosphorylation following transient cerebral ischemia in mice.Neuroscience. 2006 Oct 27;142(3):789-97. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.06.064. Epub 2006 Aug 28. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16935431
-
Involvement of gamma protein kinase C in estrogen-induced neuroprotection against focal brain ischemia through G protein-coupled estrogen receptor.J Neurochem. 2005 May;93(4):883-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03080.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15857391
-
Ibudilast, a phosphodiesterase inhibitor with anti-inflammatory activity, protects against ischemic brain injury in rats.Brain Res. 2012 Jan 11;1431:97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.11.007. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Brain Res. 2012. PMID: 22137656
Cited by
-
Exploring Structural and Molecular Features of Sciatic Nerve Lesions in Diabetic Neuropathy: Unveiling Pathogenic Pathways and Targets.Diabetes. 2025 Jan 1;74(1):65-74. doi: 10.2337/db24-0493. Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 39418320 Free PMC article.
-
Challenging the role of adaptive immunity in neurotrauma: Rag1(-/-) mice lacking mature B and T cells do not show neuroprotection after closed head injury.J Neurotrauma. 2012 Apr 10;29(6):1233-42. doi: 10.1089/neu.2011.2169. Epub 2012 Apr 10. J Neurotrauma. 2012. PMID: 22335783 Free PMC article.
-
The role of complement activation in rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 21;13(2):e0192361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192361. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29466390 Free PMC article.
-
Complement in the Homeostatic and Ischemic Brain.Front Immunol. 2015 Aug 12;6:417. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00417. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26322048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The contribution of mannose binding lectin to reperfusion injury after ischemic stroke.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2011 Feb;8(1):52-63. doi: 10.2174/156720211794520260. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 21208161 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

