ABCtoolbox: a versatile toolkit for approximate Bayesian computations
- PMID: 20202215
- PMCID: PMC2848233
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-116
ABCtoolbox: a versatile toolkit for approximate Bayesian computations
Abstract
Background: The estimation of demographic parameters from genetic data often requires the computation of likelihoods. However, the likelihood function is computationally intractable for many realistic evolutionary models, and the use of Bayesian inference has therefore been limited to very simple models. The situation changed recently with the advent of Approximate Bayesian Computation (ABC) algorithms allowing one to obtain parameter posterior distributions based on simulations not requiring likelihood computations.
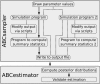
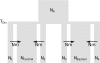
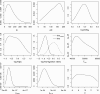
Results: Here we present ABCtoolbox, a series of open source programs to perform Approximate Bayesian Computations (ABC). It implements various ABC algorithms including rejection sampling, MCMC without likelihood, a Particle-based sampler and ABC-GLM. ABCtoolbox is bundled with, but not limited to, a program that allows parameter inference in a population genetics context and the simultaneous use of different types of markers with different ploidy levels. In addition, ABCtoolbox can also interact with most simulation and summary statistics computation programs. The usability of the ABCtoolbox is demonstrated by inferring the evolutionary history of two evolutionary lineages of Microtus arvalis. Using nuclear microsatellites and mitochondrial sequence data in the same estimation procedure enabled us to infer sex-specific population sizes and migration rates and to find that males show smaller population sizes but much higher levels of migration than females.
Conclusion: ABCtoolbox allows a user to perform all the necessary steps of a full ABC analysis, from parameter sampling from prior distributions, data simulations, computation of summary statistics, estimation of posterior distributions, model choice, validation of the estimation procedure, and visualization of the results.
Figures
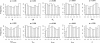
Similar articles
-
Complex genetic admixture histories reconstructed with Approximate Bayesian Computation.Mol Ecol Resour. 2021 May;21(4):1098-1117. doi: 10.1111/1755-0998.13325. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Mol Ecol Resour. 2021. PMID: 33452723 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of evolutionary parameters using short, random and partial sequences from mixed samples of anonymous individuals.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Nov 4;16:357. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0810-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26536860 Free PMC article.
-
Inference on population history and model checking using DNA sequence and microsatellite data with the software DIYABC (v1.0).BMC Bioinformatics. 2010 Jul 28;11:401. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-401. BMC Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20667077 Free PMC article.
-
On the use of kernel approximate Bayesian computation to infer population history.Genes Genet Syst. 2015;90(3):153-62. doi: 10.1266/ggs.90.153. Genes Genet Syst. 2015. PMID: 26510570 Review.
-
ABC as a flexible framework to estimate demography over space and time: some cons, many pros.Mol Ecol. 2010 Jul;19(13):2609-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2010.04690.x. Epub 2010 Jun 18. Mol Ecol. 2010. PMID: 20561199 Review.
Cited by
-
Ancient mitochondrial diversity reveals population homogeneity in Neolithic Greece and identifies population dynamics along the Danubian expansion axis.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 5;12(1):13474. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16745-8. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35931723 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation and inference algorithms for stochastic biochemical reaction networks: from basic concepts to state-of-the-art.J R Soc Interface. 2019 Feb 28;16(151):20180943. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2018.0943. J R Soc Interface. 2019. PMID: 30958205 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient ancestry and mutation simulation with msprime 1.0.Genetics. 2022 Mar 3;220(3):iyab229. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab229. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 34897427 Free PMC article.
-
Back to BaySICS: a user-friendly program for Bayesian Statistical Inference from Coalescent Simulations.PLoS One. 2014 May 27;9(5):e98011. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098011. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24865457 Free PMC article.
-
Bayesian inferences suggest that Amazon Yunga Natives diverged from Andeans less than 5000 ybp: implications for South American prehistory.BMC Evol Biol. 2014 Sep 30;14:174. doi: 10.1186/s12862-014-0174-3. BMC Evol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25266366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pritchard JK, Seielstad MT, Perez-Lezaun A, Feldman MW. Population growth of human Y chromosomes: a study of Y chromosome microsatellites. Mol Biol Evol. 1999;16(12):1791–1798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

