New endemic Legionella pneumophila serogroup I clones, Ontario, Canada
- PMID: 20202420
- PMCID: PMC3322000
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1603.081689
New endemic Legionella pneumophila serogroup I clones, Ontario, Canada
Abstract
The water-borne pathogen Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 (Lp1) is the most commonly reported etiologic agent of legionellosis. To examine the genetic diversity, the long-term epidemiology, and the molecular evolution of Lp1 clinical isolates, we conducted sequence-based typing on a collection of clinical isolates representing 3 decades of culture-confirmed legionellosis in Ontario, Canada. Analysis showed that the population of Lp1 in Ontario is highly diverse and combines lineages identified worldwide with local strains. Identical types were identified in sporadic and outbreak-associated strains. In the past 15 years, the incidence of some lineages distributed worldwide has tended to decrease, and local endemic clones and lineages have emerged. Comparative geographic distribution analysis suggests that some lineages are specific to eastern North America. These findings have general clinical implications for the study of Lp1 molecular evolution and for the identification of Lp1 circulating strains in North America.
Figures
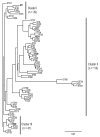



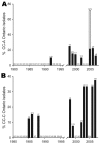

References
-
- Fraser DW, Tsai TR, Orenstein W, Parkin WE, Beecham HJ, Sharrar RG, et al. Legionnaires’ disease: description of an epidemic of pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1977;297:1189–97. - PubMed
-
- Glick TH, Gregg MB, Berman B, Mallison G, Rhodes WW Jr, Kassanoff I. Pontiac fever. An epidemic of unknown etiology in a health department: I. Clinical and epidemiologic aspects. Am J Epidemiol. 1978;107:149–60. - PubMed
-
- Euzeby JP. List of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature—genus Legionella [cited 2008 Oct 29]. http://www.bacterio.cict.fr/l/legionella.html
-
- Yu VL, Plouffe JF, Pastoris MC, Stout JE, Schousboe M, Widmer A, et al. Distribution of Legionella species and serogroups isolated by culture in patients with sporadic community-acquired legionellosis: an international collaborative survey. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:127–8. 10.1086/341087 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vergis EN, Akbas E, Yu VL. Legionella as a cause of severe pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2000;21:295–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
