Modulation of transcription factor function by O-GlcNAc modification
- PMID: 20202486
- PMCID: PMC2881704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.02.005
Modulation of transcription factor function by O-GlcNAc modification
Abstract
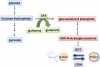
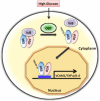
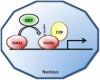
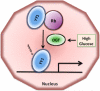
O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc) modification of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins is important for many cellular processes, and the number of proteins that contain this modification is steadily increasing. This modification is dynamic and reversible, and in some cases competes for phosphorylation of the same residues. O-GlcNAc modification of proteins is regulated by cell cycle, nutrient metabolism, and other extracellular signals. Compared to protein phosphorylation, which is mediated by a large number of kinases, O-GlcNAc modification is catalyzed only by one enzyme called O-linked N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase or OGT. Removal of O-GlcNAc from proteins is catalyzed by the enzyme beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase (O-GlcNAcase or OGA). Altered O-linked GlcNAc modification levels contribute to the establishment of many diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegeneration. Many transcription factors have been shown to be modified by O-linked GlcNAc modification, which can influence their transcriptional activity, DNA binding, localization, stability, and interaction with other co-factors. This review focuses on modulation of transcription factor function by O-linked GlcNAc modification.
Figures

References
-
- Torres CR, Hart GW. Topography and polypeptide distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine residues on the surfaces of intact lymphocytes. Evidence for O-linked GlcNAc. J Biol Chem. 259(1984):3308–3317. - PubMed
-
- Davis LI, Blobel G. Identification and characterization of a nuclear pore complex protein. Cell. 45(1986):699–709. - PubMed
-
- Holt GD, Hart GW. The subcellular distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine moieties. Localization of a novel protein-saccharide linkage, O-linked GlcNAc. J Biol Chem. 261(1986):8049–8057. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

