Daily dosing of tacrolimus in patients treated with HIV-1 therapy containing a ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor or raltegravir
- PMID: 20202988
- PMCID: PMC2902821
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkq054
Daily dosing of tacrolimus in patients treated with HIV-1 therapy containing a ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitor or raltegravir
Abstract
Objectives: The number of HIV-infected patients receiving orthotopic liver transplantation (OLTX) is increasing. One major challenge is the severe drug-drug interactions between immunosuppressive drugs such as tacrolimus and ritonavir-boosted HIV-1 protease inhibitors (PIs). The introduction of raltegravir, which is not metabolized by the cytochrome system, may allow concomitant treatment without dose adaptation.
Patients and methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of HIV-1-infected patients receiving tacrolimus concomitantly with different HIV therapies, including 12 h pharmacokinetic assessment of drug levels.
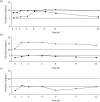
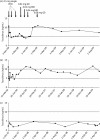
Results: Three OLTX patients received a ritonavir-boosted PI therapy when tacrolimus was added at very low doses of 0.06, 0.03 and 0.08 mg daily. Median tacrolimus blood levels were 6.6, 3.0 and 7.9 ng/mL over a follow-up period of 8, 22 and 33 months, respectively. In two other patients (one after OLTX and one with Crohn's disease), a raltegravir-based HIV therapy was started while patients received 1 or 2 mg of tacrolimus twice daily. No tacrolimus dose adjustment was necessary and drug levels remained unchanged.
Conclusions: Decreasing the dose of tacrolimus to 0.03-0.08 mg daily in patients with concomitant boosted PI therapy resulted in stable tacrolimus blood levels without alteration of PI drug levels. Concomitant use of raltegravir and tacrolimus revealed no clinically relevant drug interaction.
Figures
References
-
- Sattler M, Guengerich FP, Yun CH, et al. Cytochrome P-450 3A enzymes are responsible for biotransformation of FK506 and rapamycin in man and rat. Drug Metab Dispos. 1992;20:753–61. - PubMed
-
- Vincent SH, Karanam BV, Painter SK, et al. In vitro metabolism of FK-506 in rat, rabbit, and human liver microsomes: identification of a major metabolite and of cytochrome P450 3A as the major enzymes responsible for its metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992;294:454–60. - PubMed
-
- Paterson DL, Singh N. Interactions between tacrolimus and antimicrobial agents. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;25:1430–40. - PubMed
-
- Christians U, Jacobsen W, Benet LZ, et al. Mechanisms of clinically relevant drug interactions associated with tacrolimus. Drug Metab Dispos. 2003;31:1292–5. - PubMed
-
- van Heeswijk RP, Veldkamp A, Mulder JW, et al. Combination of protease inhibitors for the treatment of HIV-1-infected patients: a review of pharmacokinetics and clinical experience. Antivir Ther. 2001;6:201–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

