Minireview: steroidogenic factor 1: its roles in differentiation, development, and disease
- PMID: 20203099
- PMCID: PMC5417463
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0519
Minireview: steroidogenic factor 1: its roles in differentiation, development, and disease
Abstract
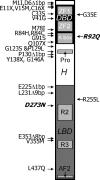
The orphan nuclear receptor steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1, also called Ad4BP, encoded by the NR5A1 gene) is an essential regulator of endocrine development and function. Initially identified as a tissue-specific transcriptional regulator of cytochrome P450 steroid hydroxylases, studies of both global and tissue-specific knockout mice have demonstrated that SF-1 is required for the development of the adrenal glands, gonads, and ventromedial hypothalamus and for the proper functioning of pituitary gonadotropes. Many genes are transcriptionally regulated by SF-1, and many proteins, in turn, interact with SF-1 and modulate its activity. Whereas mice with heterozygous mutations that disrupt SF-1 function have only subtle abnormalities, humans with heterozygous SF-1 mutations can present with XY sex reversal (i.e. testicular failure), ovarian failure, and occasionally adrenal insufficiency; dysregulation of SF-1 has been linked to diseases such as endometriosis and adrenocortical carcinoma. The current state of knowledge of this important transcription factor will be reviewed with a particular emphasis on the pioneering work on SF-1 by the late Keith Parker.
Figures
References
-
- Handler JD, Schimmer BP, Flynn TR, Szyf M, Seidman JG, Parker KL1988. An enhancer element and a functional cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase are required for expression of adrenocortical 21-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem 263:13068–13073 - PubMed
-
- Parker KL, Schimmer BP, Chaplin DD, Seidman JG1986. Characterization of a regulatory region of the steroid 21-hydroxylase gene. J Biol Chem 261:15353–15355 - PubMed
-
- Parker KL, Schimmer BP1997. Steroidogenic factor 1: a key determinant of endocrine development and function. Endocr Rev 18:361–377 - PubMed
-
- Lala DS, Rice DA, Parker KL1992. Steroidogenic factor 1, a key regulator of steroidogenic enzyme expression, is the mouse homolog of Fushi Tarazu-Factor 1. Mol Endocrinol 6:1249–1258 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

