Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae: classification, imaging findings, and clinical relevance
- PMID: 20203111
- PMCID: PMC7964015
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A2036
Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae: classification, imaging findings, and clinical relevance
Abstract
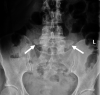
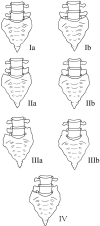
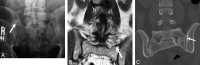
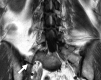
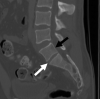
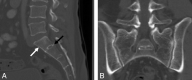
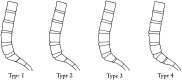
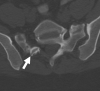
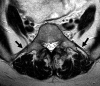
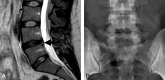
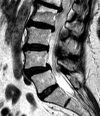
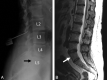
LSTVs are common within the spine, and their association with low back pain has been debated in the literature for nearly a century. LSTVs include sacralization of the lowest lumbar vertebral body and lumbarization of the uppermost sacral segment. These vertebral bodies demonstrate varying morphology, ranging from broadened transverse processes to complete fusion. Low back pain associated with an LSTV may arise from the level above the transition, the contralateral facet when unilateral, and/or the anomalous articulation when present. Although this association is still somewhat controversial, beyond dispute is the importance of identifying an LSTV in patients in whom a surgical or interventional procedure is planned. This is essential to avoid an intervention or surgery at an incorrect level. In this article, each of these issues will be addressed with attention to identifying and correctly numbering LSTVs as well as detecting imaging findings related to the genesis of low back pain.
Figures





References
-
- Bron JL, van Royen BJ, Wuisman PI. The clinical significance of lumbosacral transitional anomalies. Acta Orthop Belg 2007;73:687–95 - PubMed
-
- Castellvi AE, Goldstein LA, Chan DP. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae and their relationship with lumbar extradural defects. Spine 1984;9:493–95 - PubMed
-
- Chang HS, Nakagawa H. Altered function of lumbar nerve roots in patients with transitional lumbosacral vertebrae. Spine 2004;29:1632–35 - PubMed
-
- Delport EG, Cucuzzella TR, Kim N, et al. . Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae: incidence in a consecutive patient series. Pain Physician 2006;9:53–56 - PubMed
-
- Elster AD. Bertolotti's syndrome revisited: transitional vertebrae of the lumbar spine. Spine 1989;14:1373–77 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
