S-nitrosylation in cardiovascular signaling
- PMID: 20203313
- PMCID: PMC2891248
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.207381
S-nitrosylation in cardiovascular signaling
Abstract
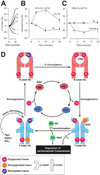
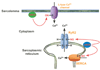
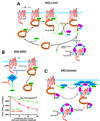
Well over 2 decades have passed since the endothelium-derived relaxation factor was reported to be the gaseous molecule nitric oxide (NO). Although soluble guanylyl cyclase (which generates cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cGMP) was the first identified receptor for NO, it has become increasingly clear that NO exerts a ubiquitous influence in a cGMP-independent manner. In particular, many, if not most, effects of NO are mediated by S-nitrosylation, the covalent modification of a protein cysteine thiol by an NO group to generate an S-nitrosothiol (SNO). Moreover, within the current framework of NO biology, endothelium-derived relaxation factor activity (ie, G protein-coupled receptor-mediated, or shear-induced endothelium-derived NO bioactivity) is understood to involve a central role for SNOs, acting both as second messengers and signal effectors. Furthermore, essential roles for S-nitrosylation have been implicated in virtually all major functions of NO in the cardiovascular system. Here, we review the basic biochemistry of S-nitrosylation (and denitrosylation), discuss the role of S-nitrosylation in the vascular and cardiac functions of NO, and identify current and potential clinical applications.
Figures

Comment in
-
Nitric oxide and the ryanodine receptor Ca-release channel.Circ Res. 2010 Jul 9;107(1):e1; author reply e2-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.221887. Circ Res. 2010. PMID: 20616330 No abstract available.
References
-
- Guyton AC, Coleman TG, Granger HJ. Circulation: overall regulation. Annu Rev Physiol. 1972;34:13–46. - PubMed
-
- McMahon TJ, Moon RE, Luschinger BP, Carraway MS, Stone AE, Stolp BW, Gow AJ, Pawloski JR, Watke P, Singel DJ, Piantadosi CA, Stamler JS. Nitric oxide in the human respiratory cycle. Nat Med. 2002;8:711–717. - PubMed
-
- Dzik S. Nitric oxide: nature's third respiratory gas. Transfusion. 2002;42:1532–1533. - PubMed
-
- Bredt DS, Snyder SH. Nitric oxide: a physiologic messenger molecule. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:175–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

