Biological therapies for cardiac arrhythmias: can genes and cells replace drugs and devices?
- PMID: 20203316
- PMCID: PMC8527570
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.212936
Biological therapies for cardiac arrhythmias: can genes and cells replace drugs and devices?
Abstract
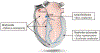
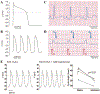
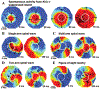
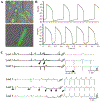
Cardiac rhythm disorders reflect failures of impulse generation and/or conduction. With the exception of ablation methods that yield selective endocardial destruction, present therapies are nonspecific and/or palliative. Progress in understanding the underlying biology opens up prospects for new alternatives. This article reviews the present state of the art in gene- and cell-based therapies to correct cardiac rhythm disturbances. We begin with the rationale for such approaches, briefly discuss efforts to address aspects of tachyarrhythmia, and review advances in creating a biological pacemaker to cure bradyarrhythmia. Insights gained bring the field closer to a paradigm shift away from devices and drugs, and toward biologics, in the treatment of rhythm disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
E.M. owns stock in Excigen, Inc which licensed intellectual property on biological pacemakers. No research funding was provided by Excigen. H.C.C. reports no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Coplen SE, Antman EM, Berlin JA, Hewitt P, Chalmers TC. Efficacy and safety of quinidine therapy for maintenance of sinus rhythm after cardioversion. A meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Circulation. 1990;82:1106–1116. - PubMed
-
- Echt DS, Liebson PR, Mitchell LB, Peters RW, ObiasManno D, Barker AH, Arensberg D, Baker A, Friedman L, Green HL, Huther ML, Richardson DW. Mortality and morbidity in patients receiving encainide, flecainide, or placebo. The Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:781–788. - PubMed
-
- Siebels J, Cappato R, Ruppel R, Schneider MA, Kuck KH. Preliminary results of the Cardiac Arrest Study Hamburg (CASH). CASH Investigators. Am J Cardiol. 1993;72:109F–113F. - PubMed
-
- Waldo AL, Camm AJ, deRuyter H, Friedman PL, MacNeil DJ, Pauls JF, Pitt B, Pratt CM, Schwartz PJ, Veltri EP. Effect of d-sotalol on mortality in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after recent and remote myocardial infarction. The SWORD Investigators. Survival With Oral d-Sotalol. Lancet. 1996;348:7–12. - PubMed
-
- Falk RH. Atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1067–1078. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

