The beta-hCG+erythropoietin in acute stroke (BETAS) study: a 3-center, single-dose, open-label, noncontrolled, phase IIa safety trial
- PMID: 20203320
- PMCID: PMC2869209
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.109.574343
The beta-hCG+erythropoietin in acute stroke (BETAS) study: a 3-center, single-dose, open-label, noncontrolled, phase IIa safety trial
Abstract
Background and purpose: Animal data suggest the use of beta-human chorionic gonadotropin followed by erythropoietin to promote brain repair after stroke. The current study directly translated these results by evaluating safety of this sequential growth factor therapy through a 3-center, single-dose, open-label, noncontrolled, Phase IIa trial.
Methods: Patients with ischemic stroke 24 to 48 hours old and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score of 6 to 24 started a 9-day course of beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (once daily on Days 1, 3, and 5 of study participation) followed by erythropoietin (once daily on Days 7, 8, and 9 of study participation). This study also evaluated performance of serially measured domain-specific end points.
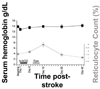
Results: A total of 15 patients were enrolled. Two deaths occurred, neither related to study medications. No safety concerns were noted among clinical or laboratory measures, including screening for deep vein thrombosis and serial measures of serum hemoglobin. In several instances, domain-specific end points provided greater insight into impairments as compared with global outcome measures.
Conclusions: Results support the safety of this sequential, 2-growth factor therapy initiated 24 to 48 hours after stroke onset.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Cramer has received consulting fees from Stem Cell Therapeutics.
Figures

References
-
- Cramer SC. Repairing the human brain after stroke. II. Restorative therapies. Ann Neurol. 2008;63:549–560. - PubMed
-
- Finklestein SP, Caday CG, Kano M, Berlove DJ, Hsu CY, Moskowitz M, Klagsbrun M. Growth factor expression after stroke. Stroke. 1990;21:III122–III124. - PubMed
-
- Carmichael ST. Gene expression changes after focal stroke, traumatic brain and spinal cord injuries. Curr Opin Neurol. 2003;16:699–704. - PubMed
-
- Kawamata T, Dietrich W, Schallert T, Gotts J, Cocke R, Benowitz L, Finklestein S. Intracisternal basic fibroblast growth factor (bfgf) enhances functional recovery and upregulates the expression of a molecular marker of neuronal sprouting following focal cerebral infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1997;94:8179–8184. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kawamata T, Ren J, Chan T, Charette M, Finklestein S. Intracisternal osteogenic protein-1 enhances functional recovery following focal stroke. Neuroreport. 1998;9:1441–1445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

