Optogenetic interrogation of neural circuits: technology for probing mammalian brain structures
- PMID: 20203662
- PMCID: PMC4503465
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2009.226
Optogenetic interrogation of neural circuits: technology for probing mammalian brain structures
Abstract
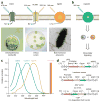
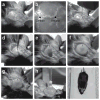
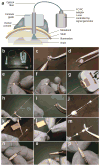
Elucidation of the neural substrates underlying complex animal behaviors depends on precise activity control tools, as well as compatible readout methods. Recent developments in optogenetics have addressed this need, opening up new possibilities for systems neuroscience. Interrogation of even deep neural circuits can be conducted by directly probing the necessity and sufficiency of defined circuit elements with millisecond-scale, cell type-specific optical perturbations, coupled with suitable readouts such as electrophysiology, optical circuit dynamics measures and freely moving behavior in mammals. Here we collect in detail our strategies for delivering microbial opsin genes to deep mammalian brain structures in vivo, along with protocols for integrating the resulting optical control with compatible readouts (electrophysiological, optical and behavioral). The procedures described here, from initial virus preparation to systems-level functional readout, can be completed within 4-5 weeks. Together, these methods may help in providing circuit-level insight into the dynamics underlying complex mammalian behaviors in health and disease.
Figures

References
-
- Boyden ES, Zhang F, Bamberg E, Nagel G, Deisseroth K. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8:1263–1268. - PubMed
-
- Zhang F, Wang LP, Boyden ES, Deisseroth K. Channelrhodopsin-2 and optical control of excitable cells. Nat Methods. 2006;3:785–792. - PubMed
-
- Zhang F, et al. Multimodal fast optical interrogation of neural circuitry. Nature. 2007;446:633–639. - PubMed
-
- Airan RD, Thompson KR, Fenno LE, Bernstein H, Deisseroth K. Temporally precise in vivo control of intracellular signalling. Nature. 2009;458:1025–1029. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

