Molecular mechanisms underlying nutrient detection by incretin-secreting cells
- PMID: 20204054
- PMCID: PMC2825293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2009.11.014
Molecular mechanisms underlying nutrient detection by incretin-secreting cells
Abstract
The hormones glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) are secreted postprandially from intestinal K- and L-cells, respectively. As incretins, these hormones stimulate insulin secretion from the pancreatic beta-cell, and have independently been implicated in the control of food intake and lipid metabolism. Whilst the enteroendocrine cells producing GIP and GLP-1 are therefore attractive targets for the treatment of diabetes and obesity, our understanding of their physiology is fairly limited. The mechanisms employed to sense the arrival of carbohydrate, fat and protein in the gut lumen have been investigated using organ perfusion techniques, primary epithelial cultures and cell line models. The recent development of mice with fluorescently labeled GIP or GLP-1-expressing cells is now enabling the use of single cell techniques to investigate stimulus-secretion coupling mechanisms. This review will focus on the current knowledge of the molecular machinery underlying nutrient sensing within K- and L-cells.
Figures
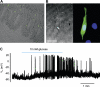
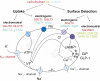
Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying nutrient-stimulated incretin secretion.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2010 Jan 5;12:e1. doi: 10.1017/S146239940900132X. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20047700 Review.
-
Incretin hormones: Their role in health and disease.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Feb;20 Suppl 1:5-21. doi: 10.1111/dom.13129. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29364588 Review.
-
Carbohydrate-induced secretion of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1.J Diabetes Investig. 2016 Apr;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):27-32. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12449. Epub 2016 Mar 14. J Diabetes Investig. 2016. PMID: 27186352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two incretin hormones GLP-1 and GIP: comparison of their actions in insulin secretion and β cell preservation.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011 Nov;107(2):248-56. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2011.07.010. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21820006 Review.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 and control of insulin secretion.Diabete Metab. 1995 Dec;21(5):311-8. Diabete Metab. 1995. PMID: 8586147 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of sucrose ingestion on brainstem and hypothalamic intrinsic oscillations in lean and obese women.Gastroenterology. 2014 May;146(5):1212-21. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.01.023. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Gastroenterology. 2014. PMID: 24480616 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Role of Bioactive Peptide Sequences in the Potential Impact of Dairy Protein Intake on Metabolic Health.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 23;21(22):8881. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228881. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33238654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optogenetic Analysis of Depolarization-Dependent Glucagonlike Peptide-1 Release.Endocrinology. 2017 Oct 1;158(10):3426-3434. doi: 10.1210/en.2017-00434. Endocrinology. 2017. PMID: 28938466 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral neural targets in obesity.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Jul;166(5):1537-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01951.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22432806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exenatide once weekly for smoking cessation: study protocol for a randomized clinical trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jan;97(2):e9567. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009567. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29480848 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Althage M.C., Ford E.L., Wang S., Tso P., Polonsky K.S., Wice B.M. Targeted ablation of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide-producing cells in transgenic mice reduces obesity and insulin resistance induced by a high fat diet. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2008;283:18365–18376. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baggio L., Drucker D. Biology of incretins: GLP-1 and GIP. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2131–2157. - PubMed
-
- Ballantyne G.H. Peptide YY(1-36) and peptide YY(3-36): Part I. Distribution, release and actions. Obesity Surgery. 2006;16:651–658. - PubMed
-
- Besterman H.S., Bloom S.R., Sarson D.L., Blackburn A.M., Johnston D.I., Patel H.R. Gut-hormone profile in coeliac disease. Lancet. 1978;15:785–788. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
