Rhombencephalitis Caused by Listeria monocytogenes in Humans and Ruminants: A Zoonosis on the Rise?
- PMID: 20204066
- PMCID: PMC2829626
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/632513
Rhombencephalitis Caused by Listeria monocytogenes in Humans and Ruminants: A Zoonosis on the Rise?
Abstract
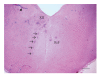
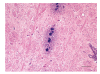
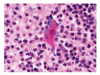
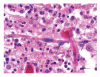
Listeriosis is an emerging zoonotic infection of humans and ruminants worldwide caused by Listeria monocytogenes (LM). In both host species, CNS disease accounts for the high mortality associated with listeriosis and includes rhombencephalitis, whose neuropathology is strikingly similar in humans and ruminants. This review discusses the current knowledge about listeric encephalitis, and involved host and bacterial factors. There is an urgent need to study the molecular mechanisms of neuropathogenesis, which are poorly understood. Such studies will provide a basis for the development of new therapeutic strategies that aim to prevent LM from invading the brain and spread within the CNS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuropathogenesis of naturally occurring encephalitis caused by Listeria monocytogenes in ruminants.Brain Pathol. 2010 Mar;20(2):378-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00292.x. Epub 2009 May 20. Brain Pathol. 2010. PMID: 19476464 Free PMC article.
-
The distribution of E-cadherin expression in listeric rhombencephalitis of ruminants indicates its involvement in Listeria monocytogenes neuroinvasion.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011 Dec;37(7):753-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2011.01183.x. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21486315
-
Ruminant organotypic brain-slice cultures as a model for the investigation of CNS listeriosis.Int J Exp Pathol. 2012 Aug;93(4):259-68. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2012.00821.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22804762 Free PMC article.
-
Listeria monocytogenes at the interface between ruminants and humans: A comparative pathology and pathogenesis review.Vet Pathol. 2022 Mar;59(2):186-210. doi: 10.1177/03009858211052659. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Vet Pathol. 2022. PMID: 34856818 Review.
-
Targeting of the central nervous system by Listeria monocytogenes.Virulence. 2012 Mar-Apr;3(2):213-21. doi: 10.4161/viru.19586. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Virulence. 2012. PMID: 22460636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dissociation of innate immune responses in microglia infected with Listeria monocytogenes.Glia. 2014 Feb;62(2):233-46. doi: 10.1002/glia.22602. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Glia. 2014. PMID: 24311463 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of Listeria monocytogenes: A trip from environmental to medical microbiology.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):2509-2545. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1975526. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34612177 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of Endemic Listeriosis to Spontaneous Abortion and Stillbirth in a Large Outdoor-housed Colony of Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta).J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2015 Jul;54(4):399-404. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2015. PMID: 26224440 Free PMC article.
-
Central nervous system Listeria monocytogenes infection mimicking central nervous system idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating disease.Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Jan 22;12:255-259. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S189930. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 30774393 Free PMC article.
-
Immunopeptidomics-based design of mRNA vaccine formulations against Listeria monocytogenes.Nat Commun. 2022 Oct 14;13(1):6075. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33721-y. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36241641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dumont J, Cotoni L. Bacille semblable à celui du rouget du porc rencontré dans le L.C.R. d’un méningitique. Annales de l’Institut Pasteur. 1921;35:625–633.
-
- Murray EGD, Webb AA, Swan MBR. A disease of rabbits characterized by a large mononuclear monocytosis caused by a hitherto undescribed bacillus Bacterium monocytogenes n. sp. Journal of Pathology & Bacteriology. 1926;29:407–439.
-
- Low JC, Donachie W. A review of Listeria monocytogenes and listeriosis. Veterinary Journal. 1997;153(1):9–29. - PubMed
-
- Schlech WF, III, Lavigne PM, Bortolussi RA, et al. Epidemic listeriosis—evidence for transmission by food. New England Journal of Medicine. 1983;308(4):203–206. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
