Critical evaluation of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) by NanoSight for the measurement of nanoparticles and protein aggregates
- PMID: 20204471
- PMCID: PMC2852530
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-010-0073-2
Critical evaluation of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) by NanoSight for the measurement of nanoparticles and protein aggregates
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) technique, compare it with dynamic light scattering (DLS) and test its performance in characterizing drug delivery nanoparticles and protein aggregates.
Methods: Standard polystyrene beads of sizes ranging from 60 to 1,000 nm and physical mixtures thereof were analyzed with NTA and DLS. The influence of different ratios of particle populations was tested. Drug delivery nanoparticles and protein aggregates were analyzed by NTA and DLS. Live monitoring of heat-induced protein aggregation was performed with NTA.
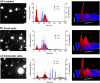
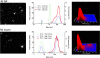
Results: NTA was shown to accurately analyze the size distribution of monodisperse and polydisperse samples. Sample visualization and individual particle tracking are features that enable a thorough size distribution analysis. The presence of small amounts of large (1,000 nm) particles generally does not compromise the accuracy of NTA measurements, and a broad range of population ratios can easily be detected and accurately sized. NTA proved to be suitable to characterize drug delivery nanoparticles and protein aggregates, complementing DLS. Live monitoring of heat-induced protein aggregation provides information about aggregation kinetics and size of submicron aggregates.
Conclusion: NTA is a powerful characterization technique that complements DLS and is particularly valuable for analyzing polydisperse nanosized particles and protein aggregates.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Nanoparticle tracking analysis of particle size and concentration detection in suspensions of polymer and protein samples: Influence of experimental and data evaluation parameters.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016 Jul;104:30-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2016.04.013. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2016. PMID: 27108267
-
Interference from Proteins and Surfactants on Particle Size Distributions Measured by Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA).Pharm Res. 2017 Apr;34(4):800-808. doi: 10.1007/s11095-017-2109-3. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28155075
-
Characterization of submicron (0.1-1 μm) particles in therapeutic proteins by nanoparticle tracking analysis.J Pharm Sci. 2015 May;104(5):1622-31. doi: 10.1002/jps.24411. Epub 2015 Mar 3. J Pharm Sci. 2015. PMID: 25737284
-
[Nanosize Particle Analysis by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(2):237-248. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00171-1. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30713234 Review. Japanese.
-
Particle tracking in drug and gene delivery research: State-of-the-art applications and methods.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Aug 30;91:70-91. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.03.017. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015. PMID: 25858664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis for the Quantification and Size Determination of Extracellular Vesicles.J Vis Exp. 2021 Mar 28;(169):10.3791/62447. doi: 10.3791/62447. J Vis Exp. 2021. PMID: 33843938 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of fragments from Autographa californica polyhedrin protein essential for self-aggregation and exogenous protein incorporation.BMC Biochem. 2015 Feb 4;16:5. doi: 10.1186/s12858-015-0034-9. BMC Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25648249 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes in disease and regeneration: biological functions, diagnostics, and beneficial effects.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Dec 1;319(6):H1162-H1180. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00075.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 28. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32986962 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on Low-Dimensional Nanomaterials: Nanofabrication, Characterization and Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Dec 29;13(1):160. doi: 10.3390/nano13010160. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36616070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viscosity of Plasma as a Key Factor in Assessment of Extracellular Vesicles by Light Scattering.Cells. 2019 Sep 6;8(9):1046. doi: 10.3390/cells8091046. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31500151 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

