Diffusion tensor imaging reliably differentiates patients with schizophrenia from healthy volunteers
- PMID: 20205252
- PMCID: PMC2896986
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.20995
Diffusion tensor imaging reliably differentiates patients with schizophrenia from healthy volunteers
Abstract
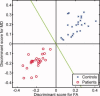
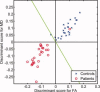
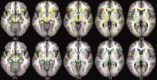
The objective of this research was to determine whether fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) maps derived from diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of the brain are able to reliably differentiate patients with schizophrenia from healthy volunteers. DTI and high resolution structural magnetic resonance scans were acquired in 50 patients with schizophrenia and 50 age- and sex-matched healthy volunteers. FA and MD maps were estimated from the DTI data and spatially normalized to the Montreal Neurologic Institute standard stereotactic space. Individuals were divided randomly into two groups of 50, a training set, and a test set, each comprising 25 patients and 25 healthy volunteers. A pattern classifier was designed using Fisher's linear discriminant analysis (LDA) based on the training set of images to categorize individuals in the test set as either patients or healthy volunteers. Using the FA maps, the classifier correctly identified 94% of the cases in the test set (96% sensitivity and 92% specificity). The classifier achieved 98% accuracy (96% sensitivity and 100% specificity) when using the MD maps as inputs to distinguish schizophrenia patients from healthy volunteers in the test dataset. Utilizing FA and MD data in combination did not significantly alter the accuracy (96% sensitivity and specificity). Patterns of water self-diffusion in the brain as estimated by DTI can be used in conjunction with automated pattern recognition algorithms to reliably distinguish between patients with schizophrenia and normal control subjects.
Hum Brain Mapp, 2010. © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Ardekani BA, Braun M, Hutton BF, Kanno I, Iida H ( 1995): A fully automatic multimodality image registration algorithm. J Comput Assist Tomogr 19: 615–623. - PubMed
-
- Ardekani BA, Strother SC, Anderson JR, Law I, Paulson OB, Kanno I, Rottenberg DA ( 1998): On the detection of activation patterns using principal components analysis In: Carson RE, Daube‐Witherspoon ME, Herscovitch P, editors. Quantitative Functional Brain Imaging with Positron Emission Tomography. San Diego: Academic Press; pp 253–237.
-
- Ardekani BA, Nierenberg J, Hoptman MJ, Javitt DC, Lim KO ( 2003): MRI study of white matter diffusion anisotropy in schizophrenia. NeuroReport 14: 2025–2029. - PubMed
-
- Ardekani BA, Guckemus S, Bachman A, Hoptman MJ, Wojtaszek M, Nierenberg J ( 2005b): Quantitative comparison of algorithms for inter‐subject registration of 3D volumetric brain MRI scans. J Neurosci Methods 142: 67–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH060004/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR018535/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R03 EB008201/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R03EB8201/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH074543/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH001990/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- M01 PR018535/PR/OCPHP CDC HHS/United States
- R01 MH076995/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH76995/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH090590/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH60374/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH01990/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH080173/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH60004/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 MH060575/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060374/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

