Effects of moniliformin and selenium on human articular cartilage metabolism and their potential relationships to the pathogenesis of Kashin-Beck disease
- PMID: 20205306
- PMCID: PMC2833404
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B0900074
Effects of moniliformin and selenium on human articular cartilage metabolism and their potential relationships to the pathogenesis of Kashin-Beck disease
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of mycotoxin moniliformin (MON) on the metabolism of aggrecan and type II collagen in human chondrocytes in vitro and the relationship between MON and Kashin-Beck disease (KBD).
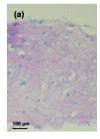
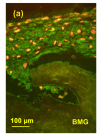
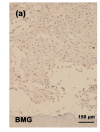
Methods: Human chondrocytes were isolated and cultured on bone matrix gelatin to form an artificial cartilage model in vitro with or without MON toxin. Cell viability was determined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. The expression of aggrecan and type II collagen in the cartilage was determined using immunocytochemical staining.
Results: MON toxin inhibited chondrocyte viability in dose-dependent and time-dependent manners. MON reduced aggrecan and type II collagen syntheses in the tissue-engineered cartilage. MON also increased the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1), MMP-13, BC4 epitopes, and CD44 in cartilages. However, the expression of 3B3(-) epitopes in cartilages was inhibited by MON. Selenium partially alleviated the damage of aggrecan induced by MON toxin.
Conclusion: MON toxin promoted the catabolism of aggrecan and type II collagen in human chondrocytes.
Figures






























Similar articles
-
Promotion of the articular cartilage proteoglycan degradation by T-2 toxin and selenium protective effect.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2008 Jan;9(1):22-33. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B071322. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2008. PMID: 18196609 Free PMC article.
-
Morphology and phenotype expression of types I, II, III, and X collagen and MMP-13 of chondrocytes cultured from articular cartilage of Kashin-Beck Disease.J Rheumatol. 2008 Apr;35(4):696-702. Epub 2008 Mar 1. J Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18322983
-
The effects of mycotoxins and selenium deficiency on tissue-engineered cartilage.Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;196(3):241-50. doi: 10.1159/000335046. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012. PMID: 22538829
-
Effects of shear stress on articular chondrocyte metabolism.Biorheology. 2000;37(1-2):95-107. Biorheology. 2000. PMID: 10912182 Review.
-
[Role of aggrecanase and MMP in cartilage degradation].Clin Calcium. 2004 Jul;14(7):38-44. Clin Calcium. 2004. PMID: 15577074 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Abnormal expression of TSG-6 disturbs extracellular matrix homeostasis in chondrocytes from endemic osteoarthritis.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 18;13:1064565. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1064565. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36468025 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of MMP-1 genetic polymorphisms and protein expression and their effects on the risk of Kashin-Beck disease in the northwest Chinese Han population.J Orthop Surg Res. 2016 May 31;11(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13018-016-0398-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016. PMID: 27245218 Free PMC article.
-
Health Risks Associated with Exposure to Filamentous Fungi.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Jul 4;14(7):719. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14070719. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28677641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum levels of PIICP, PIIANP, and PIIBNP are decreased in patients with an endemic osteochondropathy, Kashin-Beck disease.J Orthop Surg Res. 2018 May 29;13(1):128. doi: 10.1186/s13018-018-0840-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018. PMID: 29843748 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted Metabolomics Approach Correlated Enniatin B Mycotoxin Presence in Cereals with Kashin-Beck Disease Endemic Regions of China.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Aug 30;15(9):533. doi: 10.3390/toxins15090533. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755959 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cao JL, Mo XY, Wang CY. Effects of selenium and zinc on the growth metabolism of cultured chondrocytes. Chin J Endemiol. 1994;14(10):628–630. (in Chinese)
-
- Cao JL, Zheng B, Zhang SY, Mo DX. The experimental study of moniliformin effects on the chondrocytes. Endemic Dis Bull. 1995;10(4):5–7. (in Chinese)
-
- Cao JL, Zhang A, Yang B, Zhang ZT, Fu Q, Hughes CE, Caterson B. The effect of fungal moniliformin toxin and selenium supplementation on cartilage metabolism in vitro. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2007;15(Suppl. 3):C108. doi: 10.1016/S1063-4584(07)61815-9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

