Science letters: Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in mice with concanavalin A-induced hepatitis
- PMID: 20205309
- PMCID: PMC2833407
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B0900351
Science letters: Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in mice with concanavalin A-induced hepatitis
Abstract
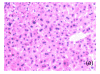
Objective: To find new protein biomarkers for the detection and evaluation of liver injury and to analyze the relationship between such proteins and disease progression in concanavalin A (Con A)-induced hepatitis.
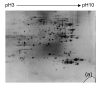
Methods: Twenty-five mice were randomly divided into five groups: an untreated group, a control group injected with phosphate buffered saline (PBS), and groups with Con A-induced hepatitis evaluated at 1, 3 and 6 h. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) and mass spectrometry (MS) were used to identify differences in protein expression among groups. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed to verify the results.
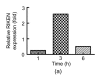
Results: In mice with Con A-induced hepatitis, expression levels of four proteins were increased: RIKEN, fructose bisphosphatase 1 (fbp1), ketohexokinase (khk), and Chain A of class pi glutathione S-transferase. Changes in fbp1 and khk were confirmed by qRT-PCR.
Conclusion: Levels of two proteins, fbp1 and khk, are clearly up-regulated in mice with Con A-induced hepatitis.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Ghrelin reduces liver impairment in a model of concanavalin A-induced acute hepatitis in mice.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Sep 28;9:5385-96. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S89096. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26451091 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the liver is under the control of nuclear factor kappa B in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008 Jul;23(7 Pt 2):e231-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2007.05083.x. Epub 2007 Aug 7. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. PMID: 17683476
-
Concanavalin-A-induced liver injury is severely impaired in mice deficient in P-selectin.J Leukoc Biol. 2002 Aug;72(2):262-70. J Leukoc Biol. 2002. PMID: 12149416
-
The differential effects of low dose and high dose concanavalin A on cytokine profile and their importance in liver injury.Inflamm Res. 2006 Apr;55(4):144-52. doi: 10.1007/s00011-006-0064-2. Inflamm Res. 2006. PMID: 16807695
-
Protection against concanavalin A-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by molsidomine is time-dependent.J Am Coll Surg. 2004 Jan;198(1):67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2003.08.014. J Am Coll Surg. 2004. PMID: 14698313
Cited by
-
In-depth identification of pathways related to cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity through an integrative method based on an informatics-assisted label-free protein quantitation and microarray gene expression approach.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012 Jan;11(1):M111.010884. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M111.010884. Epub 2011 Oct 24. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012. PMID: 22023808 Free PMC article.
-
A microarray analysis of early activated pathways in concanavalin A-induced hepatitis.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010 May;11(5):366-77. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1000020. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2010. PMID: 20443215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dominguez DC, Lopes R, Torres ML. Proteomics technology. Clin Lab Sci. 2007;20(4):239–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

