Inhibition of myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) protein inhibits ozone-induced airway neutrophilia and inflammation
- PMID: 20205598
- PMCID: PMC4064305
- DOI: 10.3109/01902140903131200
Inhibition of myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) protein inhibits ozone-induced airway neutrophilia and inflammation
Erratum in
- Exp Lung Res. 2010 Jun;36(5):321
Abstract
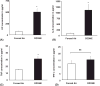
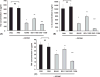
Evidence suggests inhibition of leukocyte trafficking mitigates, in part, ozone-induced inflammation. In the present study, the authors postulated that inhibition of myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS), an 82-kDa protein with multiple biological roles, could inhibit ozone-induced leukocyte trafficking and cytokine secretions. BALB/c mice (n = 5/cohort) were exposed to ozone (100 ppb) or forced air (FA) for 4 hours. MARCKS-inhibiting peptides, MANS, BIO-11000, BIO-11006, or scrambled control peptide RNS, were intratracheally administered prior to ozone exposure. Ozone selectively enhanced bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) levels of killer cells (KCs; 6 +/- 0.9-fold), interleukin-6 (IL-6; 12.7 +/- 1.9-fold), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF; 2.1 +/- 0.5-fold) as compared to cohorts exposed to FA. Additionally, ozone increased BAL neutrophils by 21% +/- 2% with no significant (P > .05) changes in other cell types. MANS, BIO-11000, and BIO-11006 significantly reduced ozone-induced KC secretion by 66% +/- 14%, 47% +/- 15%, and 71.1% +/- 14%, and IL-6 secretion by 69% +/- 12%, 40% +/- 7%, and 86.1% +/- 11%, respectively. Ozone-mediated increases in BAL neutrophils were reduced by MANS (86% +/- 7%) and BIO-11006 (84% +/- 2.5%), but not BIO-11000. These studies identify for the first time the novel potential of MARCKS protein inhibitors in abrogating ozone-induced increases in neutrophils, cytokines, and chemokines in BAL fluid. BIO-11006 is being developed as a treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) and is currently being evaluated in a phase 2 clinical study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
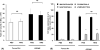
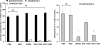

Similar articles
-
MARCKS-related peptide modulates in vivo the secretion of airway Muc5ac.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 Sep;299(3):L345-52. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00067.2010. Epub 2010 Jun 11. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010. Retraction in: Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Oct 1;309(7):L750. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.zh5-6863-retr.2015. PMID: 20543006 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
An Inhaled Inhibitor of Myristoylated Alanine-Rich C Kinase Substrate Reverses LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Nov;55(5):617-622. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0236RC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27556883 Free PMC article.
-
MARCKS protein is a potential target in a naturally occurring equine model of neutrophilic asthma.Respir Res. 2025 Apr 2;26(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12931-025-03194-w. Respir Res. 2025. PMID: 40176021 Free PMC article.
-
Patent landscape highlighting therapeutic implications of peptides targeting myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase-C substrate (MARCKS).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2023 Jan-Jun;33(6):445-454. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2023.2240020. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2023. PMID: 37526024 Review.
-
Identification of myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) in astrocytes.Front Biosci. 2005 Jan 1;10:160-5. doi: 10.2741/1517. Print 2005 Jan 1. Front Biosci. 2005. PMID: 15574358 Review.
Cited by
-
A myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate-related peptide suppresses cytokine mRNA and protein expression in LPS-activated canine neutrophils.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013 Mar;48(3):314-21. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0278OC. Epub 2012 Dec 6. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23221047 Free PMC article.
-
MARCKS and Lung Disease.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019 Jan;60(1):16-27. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0285TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30339463 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A peptide against the N-terminus of myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate promotes neuronal differentiation in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells.J Vet Med Sci. 2024 Nov 1;86(11):1136-1144. doi: 10.1292/jvms.24-0276. Epub 2024 Sep 27. J Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39343539 Free PMC article.
-
Trichostatin A abrogates airway constriction, but not inflammation, in murine and human asthma models.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 Feb;46(2):132-8. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0276OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22298527 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological roles of myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) in hematological malignancies.Biomark Res. 2021 May 6;9(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00286-9. Biomark Res. 2021. PMID: 33958003 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Koren HS, Devlin RB, Graham DE, Mann R, McGee MP, Horstman DH, Kozumbo WJ, Becker S, House DE, Mc-Donnell WF, et al. Ozone-induced inflammation in the lower airways of human subjects. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989;139:407–415. - PubMed
-
- Devlin RB, McKinnon KP, Noah T, Becker S, Koren HS. Ozone-induced release of cytokines and fibronectin by alveolar macrophages and airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1994;266:L612–L619. - PubMed
-
- Fabbri LM, Aizawa H, Alpert SE, Walters EH, O’Byrne PM, Gold BD, Nadel JA, Holtzman MJ. Airway hyperresponsiveness and changes in cell counts in bronchoalveolar lavage after ozone exposure in dogs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984;129:288–291. - PubMed
-
- Bhalla DK, Reinhart PG, Bai C, Gupta SK. Amelioration of ozone-induced lung injury by anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Toxicol Sci. 2002;69:400–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
