Creatine supplementation spares muscle glycogen during high intensity intermittent exercise in rats
- PMID: 20205834
- PMCID: PMC2825211
- DOI: 10.1186/1550-2783-7-6
Creatine supplementation spares muscle glycogen during high intensity intermittent exercise in rats
Abstract
Background: The effects of creatine (CR) supplementation on glycogen content are still debatable. Thus, due to the current lack of clarity, we investigated the effects of CR supplementation on muscle glycogen content after high intensity intermittent exercise in rats.
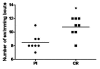
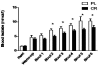
Methods: First, the animals were submitted to a high intensity intermittent maximal swimming exercise protocol to ensure that CR-supplementation was able to delay fatigue (experiment 1). Then, the CR-mediated glycogen sparing effect was examined using a high intensity intermittent sub-maximal exercise test (fixed number of bouts; six bouts of 30-second duration interspersed by two-minute rest interval) (experiment 2). For both experiments, male Wistar rats were given either CR supplementation or placebo (Pl) for 5 days.
Results: As expected, CR-supplemented animals were able to exercise for a significant higher number of bouts than Pl. Experiment 2 revealed a higher gastrocnemius glycogen content for the CR vs. the Pl group (33.59%). Additionally, CR animals presented lower blood lactate concentrations throughout the intermittent exercise bouts compared to Pl. No difference was found between groups in soleus glycogen content.
Conclusion: The major finding of this study is that CR supplementation was able to spare muscle glycogen during a high intensity intermittent exercise in rats.
Figures

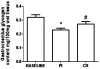
References
-
- Gualano B, Novaes RB, Artioli GG, Freire TO, Coelho DF, Scagliusi FB, Rogeri PS, Roschel H, Ugrinowitsch C, Lancha AH Jr. Effects of creatine supplementation on glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in sedentary healthy males undergoing aerobic training. Amino Acids. 2008;34:245–250. doi: 10.1007/s00726-007-0508-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Harris RC, Soderlund K, Hultman E. Elevation of creatine in resting and exercised muscle of normal subjects by creatine supplementation. Clin Sci (Lond) 1992;83:367–374. - PubMed
-
- Terjung RL, Clarkson P, Eichner ER, Greenhaff PL, Hespel PJ, Israel RG, Kraemer WJ, Meyer RA, Spriet LL, Tarnopolsky MA, Wagenmakers AJ, Williams MH. American College of Sports Medicine roundtable. The physiological and health effects of oral creatine supplementation. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2000;32:706–717. doi: 10.1097/00005768-200003000-00024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Robinson TM, Sewell DA, Hultman E, Greenhaff PL. Role of submaximal exercise in promoting creatine and glycogen accumulation in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol. 1999;87:598–604. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
