Sedentary subjects have higher PAI-1 and lipoproteins levels than highly trained athletes
- PMID: 20205861
- PMCID: PMC2826310
- DOI: 10.1186/1758-5996-2-7
Sedentary subjects have higher PAI-1 and lipoproteins levels than highly trained athletes
Abstract
Physical exercise protects against the development of cardiovascular disease, partly by lowering plasmatic total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and increased HDL-cholesterol levels. In addition, it is now established that reduction plasmatic adiponectin and increased C-reactive protein (CRP) and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) levels play a role in the maintenance of an inflammatory state and in the development of cardiovascular disease. This study aimed to examine plasma lipid profile and inflammatory markers levels in individual with sedentary lifestyle and/or highly trained athletes at rest.
Methods: Fourteen male subjects (sedentary lifestyle n = 7 and highly trained athletes n = 7) were recruited. Blood samples were collected after an overnight fast (approximately 12 h). The plasmatic lipid profile (Triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, total cholesterol, LDL-oxidized and total cholesterol/HDL-c ratio), glucose, adiponectin, C - reactive protein and PAI-1 levels were determined.
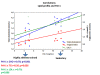
Results: Total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, TG and PAI-1 levels were lower in highly trained athletes group in relation to sedentary subjects (p < 0.01). In addition, we observed a positive correlation between PAI-1 and total cholesterol (r = 0.78; p < 0.0009), PAI-1 and LDL-c (r = 0.69; p < 0.006) and PAI-1 and TG levels (r = 0.56; p < 0.03). The plasma concentration of adiponectin, CRP, glucose, HDL-cholesterol and total cholesterol/HDL-c ratio levels were not different. These results indicate that lifestyle associated with high intensity and high volume exercise induces changes favourable in the lipid profile and PAI-1 levels and may reduce risk cardiovascular diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endotoxin levels correlate positively with a sedentary lifestyle and negatively with highly trained subjects.Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Aug 4;9:82. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-82. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20684772 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of high and low intensity aerobic conditioning programs on blood fibrinolysis and lipid profile.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1996 Jun;7(4):484-90. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199606000-00009. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1996. PMID: 8840002
-
Fibrinogen, coagulation factor VII, tissue plasminogen activator, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, and lipid as cardiovascular risk factors in chronic hemodialysis and continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients.Am J Kidney Dis. 1996 Jun;27(6):848-54. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(96)90523-5. Am J Kidney Dis. 1996. PMID: 8651250
-
The influence of exercise on the concentrations of triglyceride and cholesterol in human plasma.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1984;12:205-44. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1984. PMID: 6376133 Review.
-
Pharmacodynamic effects of oral contraceptive steroids on biochemical markers for arterial thrombosis. Studies in non-diabetic women and in women with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.Dan Med Bull. 2002 Feb;49(1):43-60. Dan Med Bull. 2002. PMID: 11894723 Review.
Cited by
-
Endotoxin levels correlate positively with a sedentary lifestyle and negatively with highly trained subjects.Lipids Health Dis. 2010 Aug 4;9:82. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-82. Lipids Health Dis. 2010. PMID: 20684772 Free PMC article.
-
Low and moderate, rather than high intensity strength exercise induces benefit regarding plasma lipid profile.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2010 May 21;2:31. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-2-31. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2010. PMID: 20492685 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid transfers to HDL are diminished in long-term bedridden patients: association with low HDL-cholesterol and increased inflammatory markers.Lipids. 2017 Aug;52(8):703-709. doi: 10.1007/s11745-017-4274-x. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28660528
-
Is exercise a therapeutic tool for improvement of cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus? A randomised controlled trial.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2010 Jul 11;2(1):47. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-2-47. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2010. PMID: 20618996 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Acute and Chronic High-Intensity Intermittent Aerobic Plus Strength Exercise on BDNF, Lipid and Autonomic Parameters.J Sports Sci Med. 2019 Jun 1;18(2):359-368. eCollection 2019 Jun. J Sports Sci Med. 2019. PMID: 31191107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamburg NM, McMackin CJ, Huang AL, Shenouda SM, Widlansky ME, Schulz E, Gokce N, Ruderman NB, Keaney JF Jr, Vita JA. Physical inactivity rapidly induces insulin resistance and microvascular dysfunction in healthy volunteers. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2007;27(12):2650–6. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.153288. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Páramo JA, Olavide I, Barba J, Montes R, Panizo C, Muñoz MC, Rocha E. Long-term cardiac rehabilitation program favorably influences fibrinolysis and lipid concentrations in acute myocardial infarction. Haematologica. 1998;83(6):519–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous