Comparative antilipidemic effect of N-acetylcysteine and sesame oil administration in diet-induced hypercholesterolemic mice
- PMID: 20205925
- PMCID: PMC2848040
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-23
Comparative antilipidemic effect of N-acetylcysteine and sesame oil administration in diet-induced hypercholesterolemic mice
Abstract
Background: There is an increasing number of novel antilipidemic therapies under consideration. The putative hypolipidemic effect of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and sesame oil was studied in a mouse model of dietary-induced hypercholesterolemia.
Methods: Male C57bl/6 mice were assigned to the following groups: (NC) control group, (HC) group receiving test diet supplemented with 2% cholesterol and 0.5% cholic acid for 8 weeks, (HCN) group receiving the test diet with NAC supplementation (230 mg/kg p.o.) and (HCS) group fed the test diet enriched with 10% sesame oil. Total serum cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol and triglycerides were assayed at the beginning and at the end of the experiment. Total peroxides and nitric oxide (NO) levels were measured in the serum at the end of the experiment. Hepatic and aortic lesions were evaluated by haematoxylin-eosin staining.
Results: Higher serum levels of total and LDL-cholesterol were recorded in all groups fed the high cholesterol diet. The HCN group presented reduced lipid levels compared to HC and HCS groups. No differences were observed between HCS and HC groups. Peroxide content in serum was markedly increased in mice consuming high cholesterol diet. NAC and sesame oil administration led to a significant decrease of serum lipid peroxidation in the levels of control group, whereas only NAC restored NO bioavailability. In terms of liver histology, the lesions observed in HCN group were less severe than those seen in the other high cholesterol groups.
Conclusion: Co-administration of NAC, but not sesame oil, restored the disturbed lipid profile and improved hepatic steatosis in the studied diet-induced hypercholesterolemic mice. Both agents appear to ameliorate serum antioxidant defense.
Figures
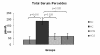


Similar articles
-
Effect of sesame oil on serum and liver lipid profiles in the rat.Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1996;66(4):386-92. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1996. PMID: 8979168
-
Impact of N-acetylcysteine and sesame oil on lipid metabolism and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis homeostasis in middle-aged hypercholesterolemic mice.Sci Rep. 2014 Oct 28;4:6806. doi: 10.1038/srep06806. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25348324 Free PMC article.
-
Antihyperlipidemic effects of Sesamum indicum L. in rabbits fed a high-fat diet.ScientificWorldJournal. 2013 Sep 4;2013:365892. doi: 10.1155/2013/365892. eCollection 2013. ScientificWorldJournal. 2013. PMID: 24082850 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of atorvastatin therapy on hypercholesterolemic rabbits with respect to oxidative stress, nitric oxide pathway and homocysteine.Life Sci. 2007 Jun 20;81(2):121-7. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.04.027. Epub 2007 May 6. Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17532348
-
Protective effect of dietary flavonoid quercetin against lipemic-oxidative hepatic injury in hypercholesterolemic rats.Pharm Biol. 2012 Aug;50(8):1019-25. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2012.655424. Pharm Biol. 2012. PMID: 22775419
Cited by
-
Enhancement of Lipid Metabolism and Hepatic Stability in Fat-Induced Obese Mice by Fermented Cucurbita moschata Extract.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Mar 13;2018:3908453. doi: 10.1155/2018/3908453. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 29725353 Free PMC article.
-
N-Acetylcysteine Treatment Restores the Protective Effect of Heart Ischemic Postconditioning in a Murine Model in the Early Stages of Atherosclerosis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 8;18(7):1014. doi: 10.3390/ph18071014. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732302 Free PMC article.
-
Hypercholesterolemia and oxidative stress inhibit endothelial cell healing after arterial injury.J Vasc Surg. 2012 Feb;55(2):489-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.07.081. Epub 2011 Nov 1. J Vasc Surg. 2012. PMID: 22047834 Free PMC article.
-
N-Acetyl Cysteine Targets Hepatic Lipid Accumulation to Curb Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in NAFLD: A Comprehensive Analysis of the Literature.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Dec 16;9(12):1283. doi: 10.3390/antiox9121283. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33339155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidants Supplementation Reduces Ceramide Synthesis Improving the Cardiac Insulin Transduction Pathway in a Rodent Model of Obesity.Nutrients. 2021 Sep 28;13(10):3413. doi: 10.3390/nu13103413. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34684414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rajamohan T, Kurup PA. Lysine: arginine ratio of a protein influences cholesterol metabolism. Part 1-Studies on sesame protein having low lysine: arginine ratio. Indian J Exp Biol. 1997;35:1218–1223. - PubMed
-
- Satchithanandam S, Chanderbhan R, Kharroubi AT, Calvert RJ, Klurfeld D, Tepper SA, Kritchevsky D. Effect of sesame oil on serum and liver lipid profiles in the rat. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 1996;66:386–392. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

