Endoscopic management of biliary fascioliasis: a case report
- PMID: 20205932
- PMCID: PMC2841078
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-1947-4-83
Endoscopic management of biliary fascioliasis: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Fasciola hepatica, an endemic parasite common in Iraq and its neighboring countries, is a very rare cause of cholestasis worldwide. Humans can become definitive hosts of this parasite through their ingestion of a contaminated water plant, for example, contaminated watercress. Symptoms of cholestasis may appear suddenly and, in some cases, are preceded by long periods of fever, eosinophilia, and vague gastrointestinal symptoms. Here we report the case of a woman with a sudden onset of symptoms of cholangitis. Her infection was proved by endoscopic retrograde cholangiography to be due to Fasciola hepatica infestation.
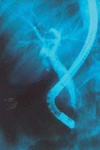
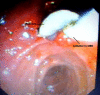
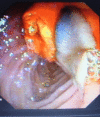
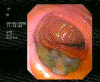
Case presentation: A 38-year-old Kurdish woman from the northern region of Iraq presented with fever, right upper quadrant abdominal pain, and jaundice. An examination of the patient revealed elevated total serum bilirubin and liver enzymes. An ultrasonography also showed a dilatation of her common bile duct. During endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, a filling defect was identified in her common bile duct. After sphincterotomy and balloon extraction, one live Fasiola hepatica was extracted and physically removed.
Conclusion: Fasciola hepatica should be a part of the differential diagnosis of common bile duct obstruction. When endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography is available, the disease can be easily diagnosed and treated.
Figures
References
-
- Adel AFM. In: Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 5. Mandell GL, Bennet JE, Dolin R, editor. Philadelphia: Churchill Livingstone; 2000. Trematodes and other flukes; pp. 2954–2956.
-
- Marsden PD. In: Diseases of the Liver. Shiff, editor. Philadelphia: Lippincott William and Wilkins; 1999. Parasitic disease of the liver; pp. 1078–1088.
-
- Barrett-Conner E. In: Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology. 2. Braude AI, editor. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; 1986. Fluke infections; pp. 979–982.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources