Comparative analysis of cell death induction by Taurolidine in different malignant human cancer cell lines
- PMID: 20205945
- PMCID: PMC2846881
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-21
Comparative analysis of cell death induction by Taurolidine in different malignant human cancer cell lines
Abstract
Background: Taurolidine (TRD) represents an anti-infective substance with anti-neoplastic activity in many malignant cell lines. So far, the knowledge about the cell death inducing mechanisms and pathways activated by TRD is limited. The aim of this study was therefore, to perform a comparative analysis of cell death induction by TRD simultaneously in different malignant cell lines.
Materials and methods: Five different malignant cell lines (HT29/Colon, Chang Liver/Liver, HT1080/fibrosarcoma, AsPC-1/pancreas and BxPC-3/pancreas) were incubated with increasing concentrations of TRD (100 microM, 250 microM and 1000 microM) for 6 h and 24 h. Cell viability, apoptosis and necrosis were analyzed by FACS analysis (Propidiumiodide/AnnexinV staining). Additionally, cells were co-incubated with the caspase Inhibitor z-VAD, the radical scavenger N-Acetylcystein (NAC) and the Gluthation depleting agent BSO to examine the contribution of caspase activation and reactive oxygen species in TRD induced cell death.
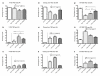
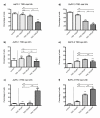
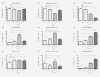
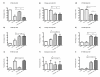
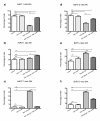
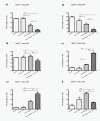
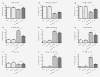
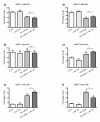
Results: All cell lines were susceptible to TRD induced cell death without resistance toward this anti-neoplastic agent. However, the dose response effects were varying largely between different cell lines. The effect of NAC and BSO co-treatment were highly different among cell lines--suggesting a cell line specific involvement of ROS in TRD induced cell death. Furthermore, impact of z-VAD mediated inhibition of caspases was differing strongly among the cell lines.
Conclusion: This is the first study providing a simultaneous evaluation of the anti-neoplastic action of TRD across several malignant cell lines. The involvement of ROS and caspase activation was highly variable among the five cell lines, although all were susceptible to TRD induced cell death. Our results indicate, that TRD is likely to provide multifaceted cell death mechanisms leading to a cell line specific diversity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene expression analysis of cell death induction by taurolidine in different malignant cell lines.BMC Cancer. 2010 Oct 30;10:595. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-10-595. BMC Cancer. 2010. PMID: 21034493 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of taurolidine, a novel antineoplastic agent, on human malignant mesothelioma.Clin Cancer Res. 2004 Nov 15;10(22):7655-61. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-0196-03. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15569998
-
Induction of reactive oxygen intermediates-dependent programmed cell death in human malignant ex vivo glioma cells and inhibition of the vascular endothelial growth factor production by taurolidine.J Neurosurg. 2005 Jun;102(6):1055-68. doi: 10.3171/jns.2005.102.6.1055. J Neurosurg. 2005. PMID: 16028765
-
Taurolidine--a new drug with anti-tumor and anti-angiogenic effects.Anticancer Drugs. 2005 Oct;16(9):917-21. doi: 10.1097/01.cad.0000176502.40810.b0. Anticancer Drugs. 2005. PMID: 16162968 Review.
-
Redox-directed cancer therapeutics: Taurolidine and Piperlongumine as broadly effective antineoplastic agents (review).Int J Oncol. 2014 Oct;45(4):1329-36. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2566. Epub 2014 Jul 28. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25175943 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism and rational combinations with GP-2250, a novel oxathiazine derivative, in ovarian cancer.Cancer Med. 2024 Aug;13(15):e70031. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70031. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39114948 Free PMC article.
-
The Antiseptic and Antineoplastic Agent Taurolidine Modulates Key Leukocyte Functions.In Vivo. 2022 Sep-Oct;36(5):2074-2082. doi: 10.21873/invivo.12933. In Vivo. 2022. PMID: 36099103 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of taurolidine alone and in combination with doxorubicin or carboplatin in canine osteosarcoma in vitro.BMC Vet Res. 2013 Jan 18;9:15. doi: 10.1186/1746-6148-9-15. BMC Vet Res. 2013. PMID: 23331343 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term treatment with taurolidine is associated with liver injury.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017 Aug 11;18(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s40360-017-0168-z. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28800748 Free PMC article.
-
Taurolidine cooperates with antineoplastic drugs in neuroblastoma cells.Genes Cancer. 2014 Nov;5(11-12):460-9. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.36. Genes Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25568670 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

