Elevation of IL-6 in the allergic asthmatic airway is independent of inflammation but associates with loss of central airway function
- PMID: 20205953
- PMCID: PMC2842243
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-28
Elevation of IL-6 in the allergic asthmatic airway is independent of inflammation but associates with loss of central airway function
Abstract
Background: Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airway that is characterized by a Th2-type of immune response with increasing evidence for involvement of Th17 cells. The role of IL-6 in promoting effector T cell subsets suggest that IL-6 may play a functional role in asthma. Classically IL-6 has been viewed as an inflammatory marker, along with TNFalpha and IL-1beta, rather than as regulatory cytokine.
Objective: To investigate the potential relationship between IL-6 and other proinflammatory cytokines, Th2/Th17 cytokines and lung function in allergic asthma, and thus evaluate the potential role of IL-6 in this disease.
Methods: Cytokine levels in induced sputum and lung function were measured in 16 healthy control and 18 mild-moderate allergic asthmatic subjects.
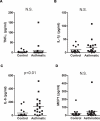
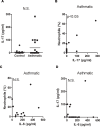
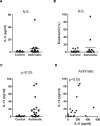
Results: The levels of the proinflammatory biomarkers TNFalpha and IL-1beta were not different between the control and asthmatic group. In contrast, IL-6 levels were specifically elevated in asthmatic subjects compared with healthy controls (p < 0.01). Hierarchical regression analysis in the total study cohort indicates that the relationship between asthma and lung function could be mediated by IL-6. Among Th2 cytokines only IL-13 (p < 0.05) was also elevated in the asthmatic group, and positively correlated with IL-6 levels (rS = 0.53, p < 0.05).
Conclusions: In mild-moderate asthma, IL-6 dissociates from other proinflammatory biomarkers, but correlates with IL-13 levels. Furthermore, IL-6 may contribute to impaired lung function in allergic asthma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Amelioration of allergic airway inflammation in mice by regulatory IL-35 through dampening inflammatory dendritic cells.Allergy. 2015 Aug;70(8):921-32. doi: 10.1111/all.12631. Epub 2015 May 15. Allergy. 2015. PMID: 25869299
-
Purinergic receptor type 6 contributes to airway inflammation and remodeling in experimental allergic airway inflammation.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011 Jul 15;184(2):215-23. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201011-1762OC. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011. PMID: 21512170
-
BuShenYiQi Formula strengthens Th1 response and suppresses Th2-Th17 responses in RSV-induced asthma exacerbated mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 May 28;154(1):131-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.041. Epub 2014 Apr 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24704667
-
Allergic airway inflammation: unravelling the relationship between IL-37, IL-18Rα and Tir8/SIGIRR.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2015;9(6):739-50. doi: 10.1586/17476348.2015.1109452. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2015. PMID: 26561030 Review.
-
The paradigm of cytokine networks in allergic airway inflammation.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Feb;15(1):41-8. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000129. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25479317 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin 6 SNP rs1800797 associates with the risk of adult-onset asthma.Genes Immun. 2016 Apr;17(3):193-8. doi: 10.1038/gene.2016.8. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Genes Immun. 2016. PMID: 26938664
-
Effects of vitamin D on inflammatory and oxidative stress responses of human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to particulate matter.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 29;13(8):e0200040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0200040. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30157189 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic overlap and immunological pathways in asthma-obstructive sleep apnea coexistence.Sleep Breath. 2025 May 7;29(2):178. doi: 10.1007/s11325-025-03341-z. Sleep Breath. 2025. PMID: 40332677
-
Inhibition of phosphodiesterase 4 modulates cytokine induction from toll like receptor activated, but not rhinovirus infected, primary human airway smooth muscle.Respir Res. 2013 Nov 15;14(1):127. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-14-127. Respir Res. 2013. PMID: 24237854 Free PMC article.
-
A new regulatory variant in the interleukin-6 receptor gene associates with asthma risk.Genes Immun. 2013 Oct;14(7):441-6. doi: 10.1038/gene.2013.38. Epub 2013 Aug 15. Genes Immun. 2013. PMID: 23945879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cromwell O, Hamid Q, Corrigan CJ, Barkans J, Meng Q, Collins PD, Kay AB. Expression and generation of interleukin-8, IL-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by bronchial epithelial cells and enhancement by IL-1 beta and tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Immunology. 1992;77(3):330–337. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

