Runx1 isoforms show differential expression patterns during hematopoietic development but have similar functional effects in adult hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 20206228
- PMCID: PMC2854264
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.02.011
Runx1 isoforms show differential expression patterns during hematopoietic development but have similar functional effects in adult hematopoietic stem cells
Abstract
Objective: RUNX1 (also known as acute myeloid leukemia 1) is an essential regulator of hematopoiesis and has multiple isoforms arising from differential splicing and utilization of two promoters. We hypothesized that the rare Runx1c isoform has a distinct role in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs).
Materials and methods: We have characterized the expression pattern of Runx1c in mouse embryos and human embryonic stem cell (hESC)-derived embryoid bodies using in situ hybridization and expression levels in mouse and human HSCs by real-time polymerase chain reaction. We then determined the functional effects of Runx1c using enforced retroviral overexpression in mouse HSCs.
Results: We observed differential expression profiles of RUNX1 isoforms during hematopoietic differentiation of hESCs. The RUNX1a and RUNX1b isoforms were expressed consistently throughout hematopoietic differentiation, whereas the RUNX1c isoform was only expressed at the time of emergence of definitive HSCs. RUNX1c was also expressed in the AGM region of E10.5 to E11.5 mouse embryos, the region where definitive HSCs arise. These observations suggested that the RUNX1c isoform may be important for the specification or function of definitive HSCs. However, using retroviral overexpression to study the effect of RUNX1 isoforms on HSCs in a gain-of-function system, no discernable functional difference could be identified between RUNX1 isoforms in mouse HSCs. Overexpression of both RUNX1b and RUNX1c induced quiescence in mouse HSCs in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: Although the divergent expression profiles of Runx1 isoforms during development suggest specific roles for these proteins at different stages of HSC maturation, we could not detect an important functional distinction in adult mouse HSCs using our assay systems.
2010 ISEH-Society for Hematology and Stem Cells. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



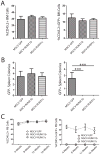
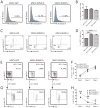

Similar articles
-
Polycomb group ring finger 1 cooperates with Runx1 in regulating differentiation and self-renewal of hematopoietic cells.Blood. 2012 May 3;119(18):4152-61. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-382390. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22411870
-
Runx1 exon 6-related alternative splicing isoforms differentially regulate hematopoiesis in mice.Blood. 2014 Jun 12;123(24):3760-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-08-521252. Epub 2014 Apr 25. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24771859 Free PMC article.
-
Mouse RUNX1C regulates premegakaryocytic/erythroid output and maintains survival of megakaryocyte progenitors.Blood. 2017 Jul 20;130(3):271-284. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-06-723635. Epub 2017 May 10. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28490570 Free PMC article.
-
Hematopoietic stem cell emergence in the conceptus and the role of Runx1.Int J Dev Biol. 2010;54(6-7):1151-63. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.103106gs. Int J Dev Biol. 2010. PMID: 20711992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the microenvironment of the embryonic aorta-gonad-mesonephros region in hematopoiesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Jun;938:109-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03579.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11458497 Review.
Cited by
-
Runx Transcription Factors in T Cells-What Is Beyond Thymic Development?Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 6;12:701924. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.701924. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34421907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Isoform-Specific RUNX1C-BTG2 Axis Governs AML Quiescence and Chemoresistance.Blood Cancer Discov. 2025 Sep 3;6(5):464-483. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-24-0327. Blood Cancer Discov. 2025. PMID: 40632085 Free PMC article.
-
The RUNX1 +24 enhancer and P1 promoter identify a unique subpopulation of hematopoietic progenitor cells derived from human pluripotent stem cells.Stem Cells. 2015 Apr;33(4):1130-41. doi: 10.1002/stem.1940. Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 25546363 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β superfamily gene expression and induction of the Runx1 transcription factor in adult neurogenic regions after brain injury.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e59250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059250. Epub 2013 Mar 21. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23555640 Free PMC article.
-
Human yolk sac-like haematopoiesis generates RUNX1-, GFI1- and/or GFI1B-dependent blood and SOX17-positive endothelium.Development. 2020 Oct 29;147(20):dev193037. doi: 10.1242/dev.193037. Development. 2020. PMID: 33028609 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Look AT. Oncogenic transcription factors in the human acute leukemias. Science. 1997;278:1059–1064. - PubMed
-
- Speck NA, Gilliland DG. Core-binding factors in haematopoiesis and leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:502–513. - PubMed
-
- Okuda T, van Deursen J, Hiebert SW, Grosveld G, Downing JR. AML1, the target of multiple chromosomal translocations in human leukemia, is essential for normal fetal liver hematopoiesis. Cell. 1996;84:321–330. - PubMed
-
- Okada H, Watanabe T, Niki M, et al. AML1(−/−) embryos do not express certain hematopoiesis-related gene transcripts including those of the PU.1 gene. Oncogene. 1998;17:2287–2293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

