Noise trauma impairs neurogenesis in the rat hippocampus
- PMID: 20206235
- PMCID: PMC2952397
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.02.071
Noise trauma impairs neurogenesis in the rat hippocampus
Abstract
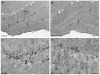
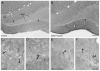
The hippocampus, a major site of neurogenesis in the adult brain, plays an important role in memory. Based on earlier observations where exposure to high-intensity noise not only caused hearing loss but also impaired memory function, it is conceivably that noise exposure may suppress hippocampal neurogenesis. To evaluate this possibility, nine rats were unilaterally exposed for 2 h to a high-intensity, narrow band of noise centered at 12 kHz at 126 dB SPL. The rats were also screened for noise-induced tinnitus, a potential stressor which may suppress neurogenesis. Five rats developed persistent tinnitus-like behavior while the other four rats showed no signs of tinnitus. Age-matched sham controls showed no signs of hearing loss or tinnitus. The inner ear and hippocampus were evaluated for sensory hair cell loss and neurogenesis 10 weeks post-exposure. All noise exposed rats showed severe loss of sensory hair cells in the noise-exposed ear, but essentially no damage in the unexposed ear. Frontal sections from the hippocampus were immunolabeled for doublecortin to identify neuronal precursor cells, or Ki67 to label proliferating cells. Noise-exposed rats showed a significant reduction of neuronal precursors and fewer dividing cells as compared to sham controls. However, we could not detect any difference between rats with behavioral evidence of tinnitus versus rats without tinnitus. These results show for the first time that high intensity noise exposure not only damages the cochlea but also causes a significant and persistent decrease in hippocampal neurogenesis that may contribute to functional deficits in memory.
Copyright 2010 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


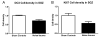
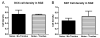
Similar articles
-
Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is impaired by transient and moderate developmental thyroid hormone disruption.Neurotoxicology. 2017 Mar;59:9-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2016.12.009. Epub 2016 Dec 31. Neurotoxicology. 2017. PMID: 28048979 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogens dynamically regulate neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult female rats.Hippocampus. 2024 Nov;34(11):583-597. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23633. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Hippocampus. 2024. PMID: 39166359
-
Acute high-intensity noise induces rapid Arc protein expression but fails to rapidly change GAD expression in amygdala and hippocampus of rats: Effects of treatment with D-cycloserine.Hear Res. 2016 Dec;342:69-79. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2016.09.010. Epub 2016 Oct 1. Hear Res. 2016. PMID: 27702572
-
Glutathione peroxidase overexpression does not rescue impaired neurogenesis in the injured immature brain.J Neurosci Res. 2009 Jun;87(8):1848-57. doi: 10.1002/jnr.21996. J Neurosci Res. 2009. PMID: 19170177 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected Consequences of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Impaired Hippocampal Neurogenesis, Memory, and Stress.Front Integr Neurosci. 2022 May 10;16:871223. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2022.871223. eCollection 2022. Front Integr Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35619926 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Loud Music and Leisure Noise Is a Common Cause of Chronic Hearing Loss, Tinnitus and Hyperacusis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Apr 16;18(8):4236. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18084236. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33923580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dental noise exposed mice display depressive-like phenotypes.Mol Brain. 2016 May 10;9(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s13041-016-0229-z. Mol Brain. 2016. PMID: 27160396 Free PMC article.
-
Early Onset Region and Cell Specific Alterations of Doublecortin Expression in the CNS of Animals with Sound Damage Induced Hearing Loss.IBRO Rep. 2019 Nov 6;7:129-140. doi: 10.1016/j.ibror.2019.10.003. eCollection 2019 Dec. IBRO Rep. 2019. PMID: 31872150 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal noise stress impairs HPA axis and cognitive performance in mice.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 5;7(1):10560. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09799-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28874680 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of age on the gap-prepulse inhibition of the cortical N1-P2 complex in humans as a step towards an objective measure of tinnitus.PLoS One. 2020 Nov 5;15(11):e0241136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0241136. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33152745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aimone JB, Wiles J, Gage FH. Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:723–727. - PubMed
-
- Andersson G, Lyttkens L, Hirvela C, Furmark T, Tillfors M, Fredrikson M. Regional cerebral blood flow during tinnitus: a PET case study with lidocaine and auditory stimulation. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000;120:967–972. - PubMed
-
- Altman J, Das GD. Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol. 1965;124:319–335. - PubMed
-
- Becker S, Wojtowicz JM. A model of hippocampal neurogenesis in memory and mood disorders. Trends Cogn Sci. 2007;11:70–76. - PubMed
-
- Belanger HG, Kretzmer T, Yoash-Gantz R, Pickett T, Tupler LA. Cognitive sequelae of blast-related versus other mechanisms of brain trauma. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2009;15:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

