Palmitoleate attenuates palmitate-induced Bim and PUMA up-regulation and hepatocyte lipoapoptosis
- PMID: 20206402
- PMCID: PMC2847010
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.01.003
Palmitoleate attenuates palmitate-induced Bim and PUMA up-regulation and hepatocyte lipoapoptosis
Abstract
Background & aims: Saturated free fatty acids induce hepatocyte lipoapoptosis. This lipotoxicity involves an endoplasmic reticulum stress response, activation of JNK, and altered expression and function of Bcl-2 proteins. The mono-unsaturated free fatty acid palmitoleate is an adipose-derived lipokine which suppresses free fatty acid-mediated lipotoxicity by unclear mechanisms. Herein we examined the mechanisms responsible for cytoprotection.
Methods: We employed isolated human and mouse primary hepatocytes, and the Huh-7 and Hep 3B cell lines for these studies. Cells were incubated in presence and absence of palmitate (16:0), stearate (18:0), and or palmitoleate (16:1, n-7).
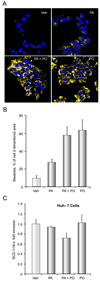
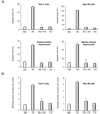
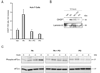
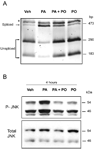
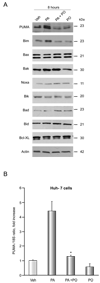
Results: Palmitoleate significantly reduced lipoapoptosis by palmitate or stearate in both primary cells and cell lines. Palmitoleate accentuated palmitate-induced steatosis in Huh-7 cells excluding inhibition of steatosis as a mechanism for reduced apoptosis. Palmitoleate inhibited palmitate induction of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response as demonstrated by reductions in CHOP expression, eIF2-alpha phosphorylation, XBP-1 splicing, and JNK activation. Palmitate increased expression of the BH3-only proteins PUMA and Bim, which was attenuated by palmitoleate. Consistent with its inhibition of PUMA and Bim induction, palmitoleate prevented activation of the downstream death mediator Bax.
Conclusions: These data suggest palmitoleate inhibits lipoapoptosis by blocking endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated increases of the BH3-only proteins Bim and PUMA.
Figures

References
-
- Angulo P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:1221–1231. - PubMed
-
- Parekh S, Anania FA. Abnormal lipid and glucose metabolism in obesity: implications for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2191–2207. - PubMed
-
- Unger RH, Orci L. Lipoapoptosis: its mechanism and its diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1585:202–212. - PubMed
-
- Feldstein AE, Gores GJ. Apoptosis in alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Front Biosci. 2005;10:3093–3099. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

